SOLAR SURGE IN INDIA
Syllabus:
GS 3 :
- Science and Technology- Developments and their Applications.
- Environmental Conservation
Focus:
India’s solar industry stands at a pivotal moment, with the government’s new policy initiatives aiming to boost domestic manufacturing while ensuring top-notch quality.
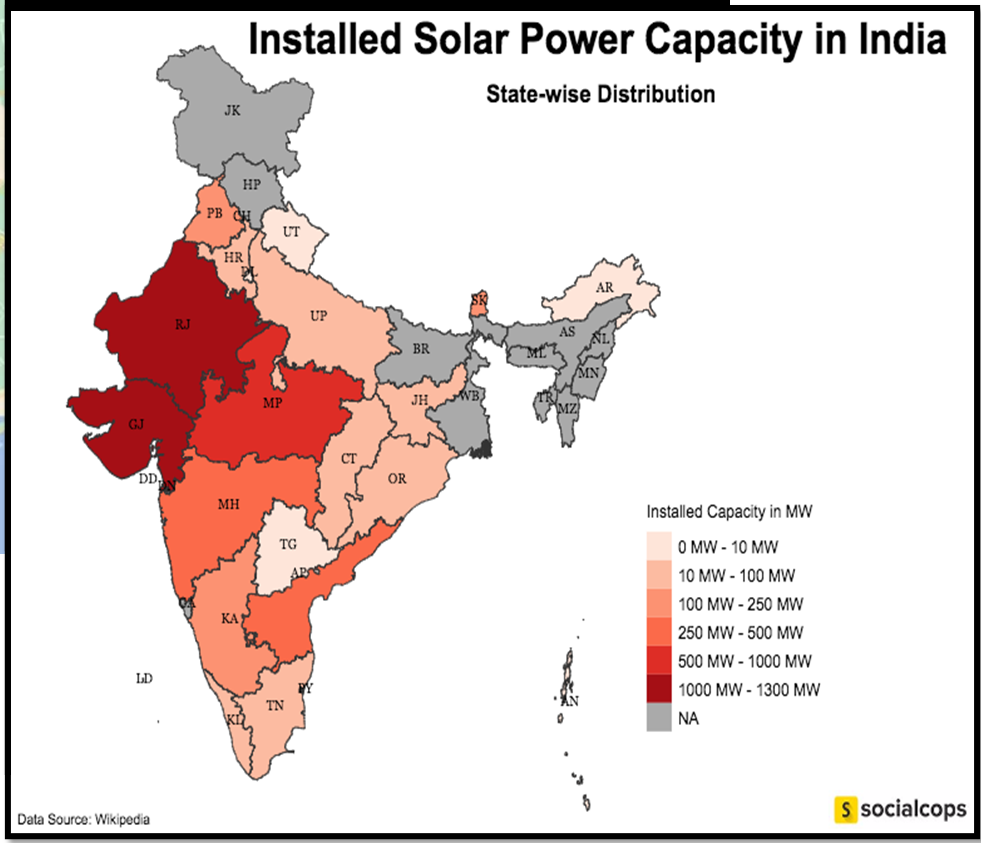
Source: Socialcops
Government’s New Policy Initiatives
- Policy Overview: The government is introducing measures to reduce reliance on imported solar panels.
- Compulsory Registration: The Approved Models and Manufacturers of Solar Photovoltaic Modules (Requirement for Compulsory Registration) Order, 2019 mandates inspections by the National Institute of Solar Energy.
- Eligibility for Government Tenders: ‘Approved’ companies can participate in government tenders, including the PM solar rooftop scheme.
- Regulation and Oversight: The policy seeks to standardize and regulate solar panel manufacturing in India.
- Incentivizing Domestic Production: To reduce import dependence, the policy offers incentives to domestic manufacturers.
- Transparency and Accountability: The new regulations aim to enhance transparency in the solar panel manufacturing sector.
| About Approved Models and Manufacturers of Solar Photovoltaic Modules
· Implemented on March 10, 2021, the MNRE enforces the “Approved Models and Manufacturers of Solar Photovoltaic Modules (Requirement for Compulsory Registration) Order, 2019” and its associated guidelines. · The order mandates the registration of Solar PV Cells and Modules manufacturers and their models post thorough inspection of their manufacturing units. · MNRE will maintain and update the Approved List of Models and Manufacturers (ALMM) Order, listing approved manufacturers and models of Solar PV Modules. Key Highlights: · Registration is valid for 2 years with an option for renewal upon document submission. · The ALMM will be regularly updated and accessible on the MNRE website. · The Ministry retains the right to conduct production, sale audits, quality tests, and facility inspections anytime for compliance checks. · Non-compliance will lead to the removal of the manufacturer from the ALMM. · Only models and manufacturers from the ALMM are eligible for Government or Government-assisted Projects and initiatives in the country. · The order aims to streamline and standardize the quality and performance of solar PV modules in India. |
Rationale Behind the Policy
- Reducing Dependence on Imports: Aim to decrease imports, particularly from China, which controls 80% of the global solar supply.
- 2030 Solar Energy Goals: India targets sourcing 500 GW of electricity from non-fossil fuel sources by 2030.
- Past Performance: Despite a 40 GW annual target, India has installed only around 13 GW in the last five years.
- COVID-19 Impact: The pandemic has been cited as a reason for the slower progress in achieving solar installation targets.
- Economic and Diplomatic Factors: The policy is influenced by economic considerations and diplomatic relations with major solar panel exporting countries.
- Domestic Industry Support: The policy aims to support and bolster the domestic solar panel manufacturing industry.
Challenges Confronting the Domestic Industry
Reliance on Imports: A significant portion of India’s solar installations is currently dependent on imported panels.
Financial Burden on Manufacturers: Domestic manufacturers face challenges in competing with cheaper Chinese imports while investing in government certification.
Implementation Delays: The government has postponed the implementation of the approved list multiple times.
Infrastructure Limitations: Limited infrastructure and production capacity hinder the growth of domestic solar panel manufacturing.
Skill Gap: A shortage of skilled labor in the manufacturing sector poses a challenge.
Supply Chain Issues: Inadequate supply chain infrastructure can impact the timely delivery of solar panels.
Market Competition: Intense competition from international manufacturers, particularly from China, affects the domestic market share.
Technological Barriers: The need for advanced technology and equipment to produce high-efficiency solar panels poses a challenge for domestic manufacturers.
Quality vs. Nationalism: The Dilemma
- Balancing Act: Promoting domestic manufacturing while maintaining high quality is a delicate balance.
- Affordability and Quality Assurance: Ensuring solar power remains affordable without compromising on quality is crucial.
- Consumer Trust: Maintaining consumer trust by delivering high-quality products is essential for the industry’s growth.
- Global Competitiveness: The industry must strive to be globally competitive in terms of both quality and cost.
- Ethical Considerations: Balancing nationalism with ethical considerations like fair trade and environmental sustainability.
- Market Dynamics: Understanding and adapting to global market dynamics without compromising on quality.
The Road Ahead: Ensuring Sustainable Growth
Global Recognition: India aims to position itself as a high-quality solar panel exporter in the global market.
Prioritizing Quality: Emphasizing rigorous quality checks and standards to build trust among consumers.
Investment in Research and Development: Investing in R&D to innovate and produce high-efficiency solar panels.
Promoting Sustainable Practices: Encouraging practices like rainwater harvesting and pond restoration to support solar energy production.
Collaboration and Partnerships: Forming partnerships with global experts to adopt best practices and technologies.
Policy Review and Adaptation: Regularly reviewing and adapting policies to meet changing industry needs and challenges.
Capacity Building: Enhancing domestic manufacturing capabilities through skill development and training programs.
Consumer Awareness: Educating consumers about the benefits of domestic solar panels to boost demand and support the industry.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Indian solar industry’s growth is promising, but maintaining this growth sustainably and with high quality is crucial. A balanced approach that supports domestic manufacturing, ensures quality, and promotes sustainable practices will be vital in achieving India’s ambitious solar energy goals.
Source:
Mains Practice Question:
Discuss the challenges facing the domestic solar manufacturing sector and the importance of maintaining a balance between growth and quality. Suggest measures for ensuring sustainable growth in the Indian solar sector.
Associated Article:
https://universalinstitutions.com/indias-solar-power-program/