INDIA TO REDUCE EV IMPORT DUTY FOR TESLA, OTHER GLOBAL AUTOMAKERS
Relevance: GS 2 – Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Why in the News?
- India has agreed to reduce import duties on electric vehicles (EVs) for global companies, including Tesla, to facilitate their entry into the Indian market.
- The reduced duty rate is slashed from 70-100% to 15% and is not exclusive to Tesla; it applies to all global EV manufacturers.
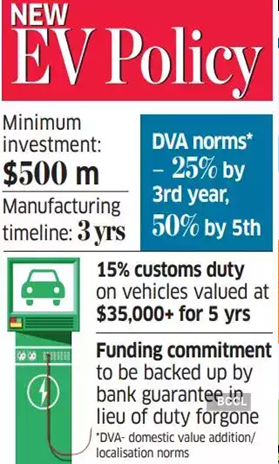
- The reduced duty is contingent upon a minimum investment of $500 million by the company.
Tesla’s Entry into India: Key Points
- Linking Investment to Concessional Imports:
- This is the first instance where investment in the auto sector in India is directly linked to concessional imports.
- Historical Precedence:
- No such concessions were provided to world’s major auto companies for conventional petrol and diesel vehicles.
- Companies like General Motors, Ford, Toyota, and Volkswagen entered the Indian market without such benefits, facing losses for decades.
- Existing EV Market:
- Many foreign and Indian companies have already launched EVs in India, suggesting that Tesla’s entry wasn’t necessary to initiate a new product line.
- Tesla’s Iconic Status: Despite the existing EV market, the GoI has conceded to Tesla due to its iconic status in the industry.
Tesla’s Market Positioning and Challenges
- Global Pricing Strategy:
- Tesla’s EVs are priced between $40,000-70,000 in the US.
- In China, Tesla has reduced prices to compete with local EV producers like BYD, Nio, XPeng, and Li Auto.
- Tesla is perceived as a luxury car brand in the US, Europe, and China, whereas the Chinese market is dominated by affordable EVs, some priced under $10,000.
- Tesla’s Product Range:
- Tesla has not yet produced an affordable mass-market car, but there are reports of R&D efforts in this direction.
- Tesla’s strengths lie in elegance, design, and new technology, crucial for the luxury segment.
- In contrast, BYD produces a comprehensive range of vehicles, from affordable to luxury, and electric buses, allowing it to surpass Tesla in terms of volume.
- Tesla’s Strategic Dilemma in India:
- If Tesla focuses on high-end cars, a significant portion of the $500 million investment will be geared towards exports rather than the Indian market, which is still developing for high-end cars.
- If Tesla opts to produce mid-priced autos for India, it will face stiff competition from existing companies, both local and global.
- Feasibility of Tesla’s Entry into India:
- Importing 8,000 cars/year of the cheapest Tesla Model 3 with the new duty benefit, estimated at Rs 39 lakh, will have a minimal impact on a market that sells a total of 4 million cars annually, with only a 2% EV penetration.
- Tesla will not benefit from the 13-18% Production Linked Incentive (PLI) benefits offered to domestic competitors like Tata Motors and Mahindra.
- Tata Motors and Mahindra plan to introduce around half a dozen EV alternatives by 2026-27, further intensifying the competition for Tesla in the Indian market.
- Competitive Landscape in India: Tata and Mahindra have ambitious EV plans and are not overly concerned about competition from Tesla due to the price gap.
- Tata has launched EVs like Tiago at ₹10 lakh ($12,000), Punch at ₹11 lakh, and Nexon at ₹15 lakh.
- Mahindra offers the XUV400 at ₹16 lakh.
- Comparison with BYD in China:
- Tesla has lost its leadership position to BYD in China.
- While Tesla produces only luxury cars, BYD offers a full range of vehicles from affordable to luxury, as well as electric buses.
- BYD also has a small plant in India.
Indian EV Policy
- Elon Musk’s Influence: Elon Musk’s persistent lobbying has influenced the Indian government’s electric vehicle policy, leading many to see the new policy as a red-carpet rollout primarily for Musk.
- The policy includes a time-bound and ceiling on the 55-85% import duty cut on electric cars above a certain value, linked to specific localization and investment milestones to boost domestic manufacturing.
- Financial and Market Considerations
- Investment Requirement: Foreign investors must commit to investing at least $500 million in India.
- Duty Concessions Details:
- Duty concessions will be applicable for five years.
- The concessions apply to 8,000 vehicles annually, priced at $35,000 or more.
- Total estimated tax concession over five years is around $800 million, as per Reuters.
- The actual cost could be lower if fewer than 8,000 vehicles are imported due to the absence of a tax cut.
- Beneficiaries of the New Policy:
- The policy benefits existing players like Tata Motors, Hyundai, VW Group, and even accelerates the plans of Phat Nhat Vuong, founder of Vietnamese OEM VinFast, which has been exploring setting up operations in Tamil Nadu.
- Reaction of Local Players:
- Initial outrage from local players has diminished following the announcement of the new policy, recognizing its broader benefits beyond just Tesla.
India’s Approach to Global EV Manufacturers
- Political Tensions Impacting Investments: Post the 2020 clashes in Ladakh, the Government of India (GoI) has restricted Chinese investments, not only in security-related sectors but also in areas like the automotive industry.
- Blocked Chinese Investments:
- Great Wall of China’s proposed $1 billion investment for conventional autos was blocked by the GoI.
- BYD’s proposal for a joint venture with Megha Engineering involving a $1 billion investment in EVs and batteries was also rejected.
- Importance of Battery Technology:
- BYD is a global leader in battery technology, critical for the cost structure of EVs.
- While Tesla and other foreign companies excel in style and features, they may struggle to compete with BYD and other Chinese companies on pricing in the price-sensitive Indian market.
- MG Motor’s Strategy in India:
- MG Motor, a global brand owned by the Chinese, has performed well in India.
- To secure its future, MG Motor plans to become a minority partner in a joint venture with Jindal South West, possibly paving the way for other top Chinese EV companies to enter the Indian market.
China’s Market in EVs
- Chinese EV Market Dominance:
- China is the world’s largest electric vehicle market.
- In 2021, one-third of all cars sold in China were battery-powered EVs or new energy vehicles (NEVs).
- Tesla’s entry in 2019-2020 significantly boosted demand and sales in the Chinese EV market.
- Market Deceleration in China:
- Over the past four years, reductions in central and local subsidies and decreased consumer spending have led to a slowdown in the growth rates of electric cars in China.
- As a result, profitability has been affected, and several EV companies like Hi-Phi, Byton, and Levdeo have faced financial difficulties.
- The number of EV brands has decreased from 196 in the past to 137 in 2023, with only 5 brands selling more than 200,000 cars, according to Shanghai-based consultant Stephen Dyer of Alix Partners.
- Future Projections for Chinese EV Market:
- Bernstein Research estimates that Chinese carmakers will add capacity for five million cars between 2023 and 2025, with most being EVs.
- Sales in China are expected to grow by approximately 3.7 million during this period.
- Warren Buffet-backed BYD plans to produce 4 million cars in China alone, surpassing its 2023 sales figure by 1 million cars.
- The Chinese commerce ministry encourages manufacturers to export cars globally, complicating geopolitical and trade dynamics.
- For instance, India held back a billion-dollar FDI proposal for BYD’s electric vehicles, despite BYD’s clean-tech commercial vehicles being operational in several Indian cities.
- The European Union launched an anti-subsidy probe against China’s growing influence in the global EV market.
Manufacturing EV in India
- Local Manufacturing Requirement in India:
- To operate in India, Tesla will need to establish manufacturing facilities in the country. Elon Musk has hinted at introducing a new mass-market compact crossover by mid-2025.
- With increasing wage inflation due to the United Auto Workers strike in the US, Musk might consider using India as a manufacturing hub to cater to the local market and as a production base for other emerging markets, similar to Ford’s strategy with its sub-compact crossover SUV, EcoSport.
- Global Slowdown in EV Market:
- The slowdown in the EV market is not confined to China; it is a global phenomenon.
- Automakers like Ford and General Motors have scaled back their electrification plans or are reconsidering gas-fired or hybrid options.
- Government Policies Impacting EV Market:
- Germany ended its electric car subsidies last December after spending 10 billion euros since 2014 on supporting the purchase of over 1 million cars.
- France excluded Chinese-made cars from any rebates around the same time, impacting Tesla’s Model 3 produced in China, though the Model Y SUV produced in Germany was exempt.
- US Market Dynamics:
- Vehicle inventories with US auto dealers reached record highs during the last Christmas holiday season, reflecting consumer weariness.
- Tesla, estimated to have sold over 50% of EVs in the US last year, reported a 47% decrease in income from operations compared to the prior year quarter.
- Operating margins for Q4 2023 were 8.2%, half of what they were in Q4 2022, and its earnings per share (EPS) of 71 cents fell short of Street estimates.
- Tesla’s stock is down 32% year-to-date.
- Elon Musk warned analysts in January of a “notably slower” growth outlook for 2024, revising down the earlier envisaged 50% average annual growth.
- Rise of Toyota’s Hybrid Vehicles:
- Toyota could potentially benefit the most from the electric vehicle trend by focusing on “headache-free” hybrids, making them more mainstream and accessible to consumers.
Source:
- https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/opinion/et-commentary/toyota-may-be-the-real-winner-indias-new-ev-policy-tailored-for-tesla-yet-challenges-remain/articleshow/108798919.cms
- https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/opinion/et-commentary/beyond-teslateslar-teslast-india-to-reduce-ev-import-duty-for-tesla-other-global-automakers/articleshow/108798832.cms?from=mdr
Mains question
Discuss the implications of India’s reduced import duties on electric vehicles and the challenges and opportunities for global EV manufacturers into the Indian market amidst global EV market dynamics. (150 words)