HIGHER ENGAGEMENT, BETTER LEARNING
Syllabus:
- GS2 : Issues Relating to Development and Management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources
Why in the News?
- The Annual Status of Education Report 2023 highlights concerning findings regarding the learning outcomes of students aged 14-18 in India.
- Despite high enrollment rates, a significant proportion of students struggle with basic reading proficiency in their regional languages, indicating a pervasive learning deficit.
Source: HT
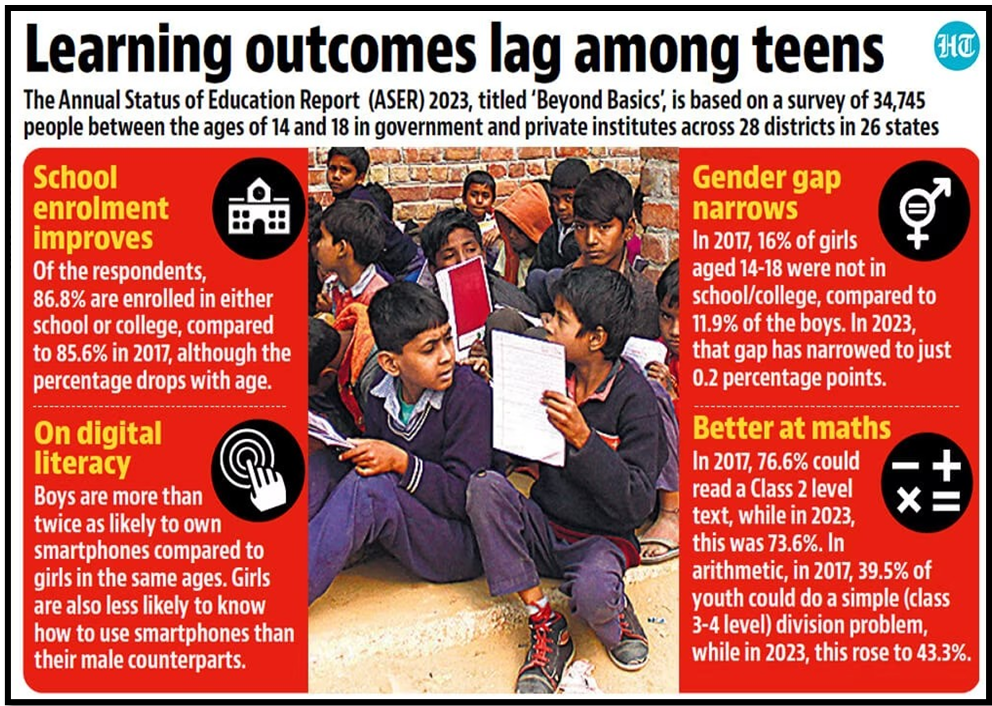
| Annual Status of Education Report (ASER)
· ASER is an annual citizen-led household survey focused on rural India’s education landscape. · It aims to assess school enrollment and learning outcomes among children. · Conducted since 2005, it’s the largest citizen-led survey in India, covering all rural districts. Key Highlights of ASER 2023: Enrolment Rates: · 86.8% of 14-18-year-olds are enrolled. · Enrolment varies by age, with 3.9% of 14-year-olds and 32.6% of 18-year-olds not enrolled. · Majority opt for Arts/Humanities streams in higher classes (55.7%). · Gender disparity exists, with fewer females (28.1%) in STEM streams compared to males (36.3%). Vocational Training: · Only 5.6% are in vocational training, more prevalent at college level (16.2%). · Short-duration courses of six months or less are common. Basic Abilities: · 25% struggle to read Class II text fluently in regional languages. · Over half face challenges with division problems. Language and Arithmetic Skills: · Females outperform males in reading but lag in arithmetic. · 57.3% can read English sentences, with 75% understanding meanings. Digital Awareness and Skills: · Nearly 90% have household smartphones. · Males (43.7%) own more smartphones than females (19.8%). · Boys excel in digital tasks; performance improves with education and reading skills. Foundational Numeracy Skills: · Over 50% face difficulties with elementary division problems. · Around 45% struggle with calculating hours based on sleep timings. Digital Education: · High Smartphone Penetration: Nearly 90% have smartphones, indicating widespread digital access. · Gender Gaps in Digital Literacy: Girls lag in smartphone and computer usage. · Online Safety Awareness: Boys show better familiarity with online safety settings. · Smartphone Usage for Education: Two-thirds use smartphones for educational purposes. · Limited Connectivity for Assessment: Not all youth have smartphones with good connectivity, showing access discrepancies. · Educational Activities Among Non-Enrolled Youth: A quarter of non-enrolled youth engage in educational activities on smartphones, highlighting their role in informal learning. |
Learning Deficit:
- Persistent Issue: India has grappled with a learning deficit for years, as evidenced by the findings of Pratham’s annual surveys. Despite growing awareness, little tangible improvement has been observed in the educational landscape.
- Low Attendance Impact: Low attendance rates in public schools contribute to the learning deficit, as many enrolled students fail to acquire meaningful knowledge and skills due to disengagement with the education system.
- Teacher-Student Engagement: Ineffective teacher-student engagement exacerbates the learning deficit, with teachers often focusing on a select few students while neglecting the broader classroom dynamic.
- Curriculum Misalignment: The curriculum often fails to cater to the diverse learning needs of students, leading to disinterest and disengagement among learners.
- Resource Constraints: Limited resources, including outdated teaching materials and overcrowded classrooms, pose significant challenges to effective learning environments.
Challenges in Classroom Dynamics:
- Rote Learning Tradition: India has a long-standing tradition of rote learning, which fails to cater to the diverse learning needs of students in a rapidly evolving world.
- Passive Learning Environment: Classroom environments often prioritize passive learning, where students passively receive information without active cognitive or emotional engagement.
- Limited Teacher Feedback: Lack of two-way communication between teachers and students impedes the customization of teaching approaches to suit individual learning preferences and needs.
- Inadequate Infrastructure: Many schools lack adequate infrastructure and resources to facilitate interactive learning experiences, further hindering student engagement.
- Socio-Economic Disparities: Socio-economic disparities contribute to unequal access to quality education, with marginalized communities facing greater barriers to meaningful learning opportunities.
Ideal Classroom Scenario:
- Active Learning: An ideal classroom fosters active learning through interactive teaching methods, peer collaboration, and hands-on learning experiences.
- Teacher Participation: Teachers play a pivotal role in facilitating student engagement by actively participating in lessons, providing real-time feedback, and creating inclusive learning environments.
- Equitable Learning Opportunities: Classroom engagement should be inclusive and accessible to all students, irrespective of their background, gender, or abilities.
- Curriculum Relevance: Curricula should be tailored to the needs and interests of students, integrating real-world examples and practical applications to enhance engagement and learning outcomes.
- Technological Integration: Leveraging technology in education can enhance student engagement, providing interactive learning tools, multimedia resources, and online platforms for collaboration and exploration.
Teacher Training and Support:
- Practical Training: Teacher education programs should prioritize practical training over theoretical lectures, providing educators with hands-on experience in learner engagement techniques.
- Continuous Professional Development: Ongoing professional development opportunities should be provided to teachers, focusing on innovative teaching methodologies, classroom management strategies, and effective assessment practices.
- Mentorship Programs: Mentorship programs can support novice teachers in navigating the complexities of student engagement, offering guidance, feedback, and best practices from experienced educators.
- Peer Learning Communities: Establishing peer learning communities allows teachers to collaborate, share insights, and learn from each other’s experiences in promoting student engagement and improving learning outcomes.
- Resource Allocation: Adequate resources should be allocated to schools for the implementation of student-centered teaching approaches, including instructional materials, technology infrastructure, and professional development initiatives.
- Community Engagement: Collaboration between schools, parents, and community stakeholders fosters a supportive learning environment and reinforces the importance of education in society.
- Policy Reform: Government policies should prioritize teacher training and support as integral components of education reform initiatives, ensuring sustained improvements in teaching quality and student outcomes.
Focus on Student Engagement:
- Structured Lessons: Structured lessons, coupled with high-quality teacher-student relationships, promote student autonomy and decision-making, enhancing overall engagement and learning outcomes.
- Classroom Dynamics: Simple changes in classroom dynamics, such as encouraging student participation, promoting interactive learning activities, and offering choices, can significantly improve the learning environment.
- Assessment Practices: Assessment methods should be designed to assess not only content knowledge but also critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving skills, fostering a culture of active learning and continuous improvement.
- Parental Involvement: Engaging parents in their children’s education can enhance student motivation and academic achievement, fostering partnerships between schools, families, and communities.
- Holistic Development: Education should aim to nurture the holistic development of students, including cognitive, emotional, social, and physical aspects, fostering lifelong learning and personal growth.
Way Forward:
- Policy Implications: It’s imperative to shift the educational discourse from the Right to Education to the Right to Learning, prioritizing meaningful learning experiences over mere enrollment statistics.
- Holistic Approach: Addressing the learning deficit requires a holistic approach, encompassing teacher training, curriculum reform, and systemic changes to foster student engagement and enhance learning outcomes.
- Collaborative Efforts: Stakeholders across the education sector, including policymakers, educators, parents, and communities, must collaborate to create supportive learning environments and opportunities for all students.
- Investment in Education: Adequate investment in education infrastructure, teacher training, and curriculum development is essential to address the root causes of the learning deficit and ensure equitable access
Conclusion:
In conclusion, addressing the learning deficit in India necessitates a concerted effort to prioritize student engagement, revamp teaching practices, and provide continuous support to educators. By fostering active learning environments and empowering teachers, India can strive towards ensuring the Right to Learning for all its students.
Source:
https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/op-ed/higher-engagement-better-learning/article67945707.ece
Mains Practice Question:
Evaluate the role of teachers and curriculum relevance interventions in addressing the learning deficit and promoting a conducive learning environment for all students.