KYASANUR FOREST DISEASE (KFD): A VIRAL INFECTION
Why in the News?
- Recent cases have prompted health authorities to take preventive measures.
About Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD):
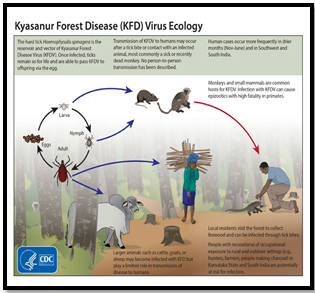
Kyasanur forest disease (KFD) is a viral hemorrhagic fever transmitted by ticks, prevalent in the south-western region of India.
- Background: Since its discovery in 1956 in Karnataka’s forests, over 560 deaths have been attributed to KFD.
Source: CDC
- Virus :It stems from a virus within the Flaviviridae family.
- Spread: Transmitted through ticks, both primates and humans can contract the disease while visiting forest areas.
- Symptoms: Onset occurs 3-8 days after a tick bite, with fever, headache, body pain, and gastrointestinal symptoms. Severe cases may involve nosebleeds.
- Prevention: The forest department distributes tick repellents like DEPA oil, and the government offers free treatment. Vaccine development efforts are underway.

 Source: CDC
Source: CDC

