SMALLER CITIZENS
Relevance: GS2 - Education
Why in the News?
- Pratham Education Foundation has been facilitating the Annual Status of Education Report (ASER) since 2005. ASER, a large-scale citizen-led household survey, aims to assess the school enrollment and learning levels of rural Indian children.
- The basic ASER survey is conducted nationwide every alternate year, focusing on children aged 3-16 years. Data collection includes information on enrollment status and basic reading and arithmetic levels for children aged 5-16 years.
- In 2023, ASER will once again spotlight the abilities of youth (14-18 years old) to apply reading and math skills in everyday situations and explore their aspirations.
Assessment Scope and Methodology:
- The household survey covered 28 districts across 26 States, providing a comprehensive understanding of the educational landscape.
- The assessment focused on 34,745 students, offering insights into their foundational reading and arithmetic abilities.
- Pandemic Impact on Children: The pandemic posed significant difficulties for India’s youngest citizens, especially children. The true extent of the impact is now emerging, revealing the lasting consequences on their education.
ASER 2023 Findings:
- ASER 2023, titled ‘Beyond Basics,’ sheds light on the educational challenges faced by children.
- A survey conducted by Pratham among rural students aged 14 to 18 reveals that more than half grapple with basic mathematics skills.
- Concerns Over Foundational Skills:
- Alarming results indicate that over 50% of students in the surveyed age group face challenges in mastering basic mathematics, typically taught in Classes 3 and 4.
- The findings highlight a concerning setback in foundational skills, emphasizing the need for targeted interventions to address learning gaps.
- Reading Proficiency:
- Approximately 25% of the 14-18 age group struggle to read a text at the Class 2 level in their mother tongue.
- This highlights a significant gap in basic reading skills among a quarter of the surveyed students.
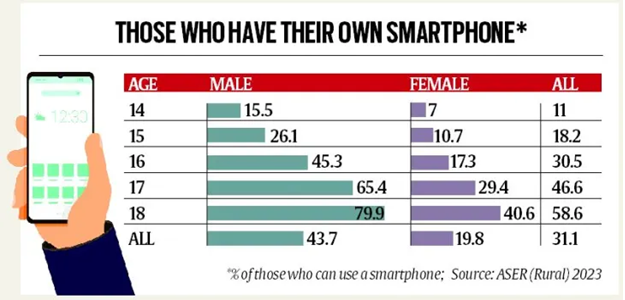
- Gender Disparities in Skills:
- Boys exhibit better skills in arithmetic and English reading compared to girls in the same age group.
- The findings emphasize gender-based differences in educational achievements, indicating areas for targeted support.
- Enrollment and Age Disparities:
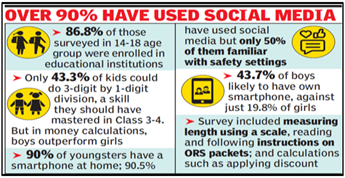
- Overall Enrollment: In the 14-18 age group, 86.8% are enrolled in educational institutions.
- Age-Related Gaps: However, as students age, disparities emerge, with 32.6% of 18-year-olds not attending school compared to 3.9% of 14-year-olds.
- Stream and Vocational Preferences:
- Stream Choices: In higher classes (Class 11 and above), Humanities is the preferred stream for the majority of students.
- Gender Disparities in Science: Girls are less likely to enroll in the science stream (28.1%) compared to boys (36.3%).
- Vocational Training: A small percentage (5.6%) opt for vocational training or related courses, indicating a lower preference for such pathways.
- Private Tuition Trends:
- Increase Over Time: The nationwide proportion of children opting for private tuition rose from 25% in 2018 to 30% in 2022.
- Educational Support: The growing reliance on private tuition suggests additional support sought outside the conventional educational system.
- Smartphone Usage and Online Safety:
- Close to 90% of surveyed youngsters possess smartphones and are familiar with their usage.
- Despite smartphone usage, many lack awareness of online safety settings, signaling a need for education on digital literacy.
Challenges in Foundational Skills:
- Reading and Arithmetic Lag: Trends reveal a significant lag in reading and solving simple arithmetic, indicating challenges in foundational skills.
- Ailing Education System: These trends provide insights into the issues affecting the education system and the need for corrective measures.
National Education Policy 2020 Goals:
- Foundational Literacy Priority: The National Education Policy 2020 emphasizes achieving universal foundational literacy and numeracy in primary school by 2025.
- State Initiatives: While states have made efforts under the NIPUN Bharat Mission, the numbers highlight the considerable catching up required in a diverse and vast country like India.
Challenges Beyond Compulsory School Cycle:
- Post-Class 8 Concerns: Rising enrollment is positive, but challenges arise after the compulsory school cycle (Class 8) due to difficulties in coping with the ambitious higher secondary curriculum.
- Gaps in Implementation: Despite the Right to Education Act, 2009 ensuring universal access, there are gaps to be addressed to fulfill its spirit for every child.
Significance of ASER Report, 2023
- Persistent Deficiencies in Foundational Skills:
- ASER reports spanning nearly two decades consistently highlight deficiencies in foundational skills like reading and basic arithmetic among children in elementary school.
- Despite awareness and efforts, the ASER 2023 underscores the enduring gap in learning outcomes, emphasizing the persistence of challenges.
- Extension to Older Age Group:
- This year’s ASER report shifts its focus to an older age group, revealing similar learning gaps among adolescents.
- The findings extend the narrative beyond elementary education, indicating ongoing struggles in basic reading and arithmetic skills even at higher levels.
- Challenges in Higher Grades:
- The report highlights that children face difficulties in mastering basic skills well into their teenage years, including when they reach Class 10 and higher secondary levels (Classes 11 and 12).
- The persistence of skill deficits among adolescents raises concerns about their preparedness for entering the job market, indicating potential challenges in employment.
- Urgent Need for Corrective Measures:
- The identified skill deficit emphasizes the urgency of implementing corrective measures to address learning gaps among adolescents.
- Given the proximity to the job market, the findings stress the importance of interventions to enhance the employability of these students.
Mains question
What is the role and scope of the Annual Status of Education Report (ASER) in evaluating rural education in India? Discuss its evolution, focus areas, and significance for policymaking.

 Relevance: GS2 - Education
Relevance: GS2 - Education