ORDER AT SEA
Relevance:
GS 2
- India and its neighbourhood- relations.
- Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
- Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests, Indian diaspora.
Why in News:
Recently, YEMEN-BASED Houthi rebels have risen after the October 7 Hamas attack on Israel to pose a serious threat to Red Seamer-chant-shipping traffic.
Source- CTECH
Importance of Naval Presence
- Global Maritime Dynamics: Shipping is vital for global trade, with the Indian Ocean as a major trade artery. Ensuring safe passage is critical for economic stability and international relations.
- India’s Maritime Role: As a significant maritime power, India’s naval presence and action in the region reflect its commitment to global maritime security and trade.
Geopolitical Context and Strategic Interests
- Regional Tensions and Conflicts: The Yemeni conflict, seen as a proxy between Saudi Arabia and Iran, complicates maritime security. It involves various regional and global players, each with strategic interests.
- India’s Diplomatic Balancing Act: India is urged to leverage its relationships with Iran and Israel to advocate for moderation and de-escalation, given the risk of a wider regional conflict affecting maritime routes.
Maritime Security Challenges
- Threats to Shipping Lanes: The Red Sea and other choke points are vulnerable to piracy, terrorism, and state-led disruptions. Recent threats and attacks underscore the volatility in key maritime zones.
- Adapting to Modern Threats: With the advent of drone warfare and sophisticated threats, navies, including India’s, must adapt with new strategies and technologies for maritime security.
- Smuggling and Trafficking: Combatting the smuggling of goods and human trafficking requires international collaboration and enhanced surveillance to uphold maritime law and security.
- Cybersecurity in Maritime Domain: The rise of technology in shipping and naval operations demands robust cybersecurity measures to protect against digital threats, ensuring the safety and integrity of maritime infrastructure.
Naval Strategy and International Law
- Jurisdiction and International Waters: The principle of the “flag state” emphasizes that a ship’s registry nation has legal authority over it in international waters, posing challenges for intervention by other naval forces.
- Naval Operations and Collaboration: India’s deployment of warships showcases its role and reassures regional partners. However, operations are limited by international law and the evolving nature of maritime threats.
Technological Evolution in Maritime Warfare
- Counter-Drone Measures and Defense: The rise of drone threats requires navies to develop countermeasures, including detection systems and soft-kill options to protect merchant and naval vessels.
Reasons for Houthi Attacks in the Red Sea
- Support for Hamas: The Houthis have declared solidarity with Hamas in response to Israel’s military operations in Gaza, particularly after the October 7 attacks by Hamas.
- Targeting Israeli Interests: The group is focusing on vessels traveling to or from Israel, intensifying attacks with drones and rockets to deter Israel and disrupt its maritime activities.
- Enhanced Attack Capabilities: Their use of advanced weaponry like drones and missiles has increased, targeting not just Israel but broadly aiming at foreign-owned vessels in the Red Sea.
Strategic Importance of the Red Sea and Bab el-Mandeb
Source: Britanica
- Red Sea Significance: A crucial global trade route, especially for Europe-Asia commerce and a significant passage for a substantial portion of the world’s oil supply.
- Bab el-Mandeb Strait: Known as the “Gate of Tears,” it’s a strategic chokepoint connecting the Red Sea to the Indian Ocean, critical for access to the Suez Canal and global shipping routes.
| Red Sea
· Location: Positioned as an inlet of the Indian Ocean nestled between Africa and Asia. · Salinity: Noted as one of the world’s most saline bodies of water. · Bordering Nations: Surrounded by Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Sudan, Eritrea, and Djibouti. · Southern Connection: Links to the Indian Ocean via the Bab el Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. · Northern Features: Bounded by the Sinai Peninsula, Gulf of Aqaba, and Gulf of Suez, leading into the Suez Canal. · Geological Aspect: Forms a segment of the expansive Great Rift Valley, specifically the Afro-Arabian Rift Valley. |
Impact of Houthi Attacks
- Military Escalation Risks: Western and regional powers may increase naval presence and potentially engage in military action to ensure the passage’s security, escalating tensions in the Middle East.
- Economic and Trade Disruptions: Attacks threaten major economic repercussions, including increased shipping costs and rerouting delays, affecting global supply chains and specifically impacting Egypt’s Suez Canal revenue.
India’s strategic position and naval capabilities place it at the forefront of ensuring maritime security in the Indian Ocean. As regional tensions and technological challenges evolve, India must continue to engage diplomatically, upgrade its maritime defense strategies, and work collaboratively with international partners to maintain peace and order at sea. This will help in safeguarding vital trade routes and promoting stability in a region pivotal to global economic health.
Source
Indian Express
Mains Question
Q Critically evaluate the role of the Indian Navy as a ‘preferred security partner’ and its diplomatic and strategic maneuvers in balancing relationships with key regional powers like Iran and Israel. Illustrate how India can enhance its maritime capabilities and diplomatic engagements to ensure a stable and secure maritime domain.”

 Source- CTECH
Source- CTECH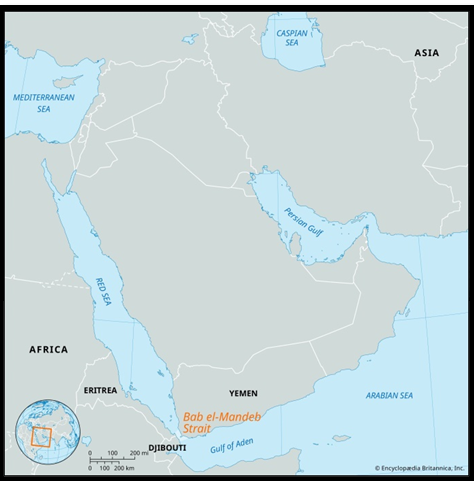 Source: Britanica
Source: Britanica

