WHO CALL FOR E-CIGARETTE CONTROL
Why in the News?
- WHO emphasizes that e-cigarettes, as consumer products, are not proven effective for population-level tobacco cessation.
- Instead, alarming evidence reveals adverse population health effects.
Source: Best in AU
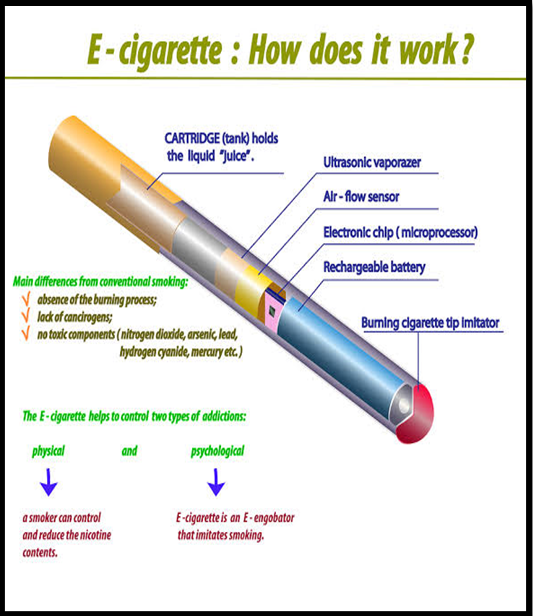
What are E-Cigarette ?
E-cigarettes, or electronic cigarettes, are battery-powered devices that heat a liquid (usually containing nicotine, flavorings, and other chemicals) to produce an aerosol, which is then inhaled. They are designed to simulate the experience of smoking traditional cigarettes but without burning tobacco.
Key Challenges :
- Addictiveness and Harm to Health:
- E-cigarettes with nicotine are highly addictive and harmful to health.
- Potential linkage to increased cigarette use is a concern.
- Recruitment of Children and Young People:
- WHO Director-General urges urgent control measures to protect children and non-smokers.
- Concerns raised about children being recruited and trapped into e-cigarette use, leading to nicotine addiction.
- Global Marketing and Regulation Gaps:
- E-cigarettes aggressively marketed globally, with 34 countries banning their sale.
- 88 countries lack a minimum age for e-cigarette purchase, and 74 countries lack regulations for these products.
Impact on Youth and Health Hazards
- Social Media Influence:
- Brief exposure to e-cigarette content on social media linked to increased intention to use and more positive attitudes.
- Young e-cigarette users are nearly three times more likely to use traditional cigarettes later in life.
- Alarming Figures on Youth Usage:
- Data reveals higher e-cigarette use rates among children (13-15 years) than adults in all WHO regions.
- Canada sees a doubling of e-cigarette use among 16 to 19-year-olds between 2017 and 2022, while the U.K. witnesses a tripling in three years.
Health Implications:
- Carcinogenic :E-cigarettes generate toxic substances, some causing cancer, and others increasing heart and lung disorder risks.
- Imbalanced Development: Adverse effects include brain development issues and learning disorders in young people.
- Foetal Risk: Foetal exposure to e-cigarettes negatively affects development.
- Bystander Risks: Emissions pose risks to bystanders, necessitating urgent measures for prevention and comprehensive tobacco control.
Way Forward:
- Urgent actions required to prevent e-cigarette uptake, counter nicotine addiction, and adopt a comprehensive tobacco control approach.
- WHO stresses the importance of tailored measures considering national circumstances.

 Source: Best in AU
Source: Best in AU


