METHANE AS A CLIMATE POLLUTANT:
Source: Hinkle Charitable Foundation
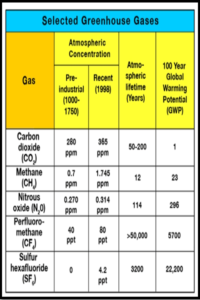
Potency and Global Warming Potential (GWP):
- Methane, represented by the chemical formula CH4, is an organic compound consisting of carbon and four hydrogen atoms.
- In climate discussions, it has gained attention for its potency as a climate pollutant compared to carbon dioxide.
- Global Warming Potential (GWP) : GWP measures the warming caused by a substance relative to the same mass of carbon dioxide.
- Methane’s GWP is significantly higher than carbon dioxide, with a GWP100 of 28.
Duration in the Atmosphere:
- Unlike carbon dioxide, which persists in the atmosphere for several decades, methane is a short-lived climate pollutant.
- The breakdown of methane occurs within a matter of years, emphasizing its less persistent nature in contributing to global warming.
Sources and COP-28 Initiatives:
- Various human activities contribute to methane emissions, including cattle-farming, landfills, wastewater treatment facilities, rice cultivation, and certain industrial processes.
- The ongoing COP-28 climate talks in the United Arab Emirates have brought increased awareness to methane’s impact on global warming.
- Philanthropic bodies like the Sequoia Climate Foundation and the Bezos Earth Fund have pledged a collective investment of $450 million to develop solutions addressing methane emissions, showcasing the growing acknowledgment of the need to tackle this environmental challenge.

 Source: Hinkle Charitable Foundation
Source: Hinkle Charitable Foundation

