Evolution of Biosphere Reserves as Beacons of Hope
Relevance
- GS paper 3 Conservation, Environmental Pollution and Degradation, Environmental Impact Assessment.
- Tags: #UPSC #GS3 #Environment #BiosphereReserve #ManAndBiosphereProgramme
Why in the news?
Biosphere Reserves: A Sanctuary for Nature and Humanity
- Amidst urban chaos, people seek refuge in places of natural beauty.
- Tourists unconsciously increase the use of single-use plastic, especially plastic water bottles.
- The prevalence of discarded plastic bottles on beaches hinders a relaxing vacation.
- Biosphere Reserves offer hope in the face of the climate crisis by preserving biodiversity, reducing pollution, and enhancing climate resilience.
- They are vibrant ecosystems where nature and humanity coexist in harmony, offering a symphony of life.
Biosphere Reserves
- Biosphere Reserves are sites established by countries and recognized under UNESCO’s Man and Biosphere (MAB) Programme to promote sustainable development based on local community efforts and sound science.
- UNESCO initiated the Biosphere Reserve program in 1971, highlighting its commitment to conserving biodiversity and natural ecosystems.
- The primary objective of biosphere reserves is to safeguard all life forms and their surrounding ecosystems in their natural habitat. These reserves serve as benchmarks for assessing changes in natural environments.
- The world’s first biosphere reserve was designated in 1979, marking the beginning of a global network of such reserves that has continued to expand.
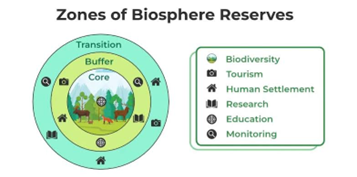
The Three Zones of a Biosphere Reserve
Biosphere Reserves are typically organized into three distinct zones:
Core Zone: The Heart of Conservation
- The core zone is the innermost region of the reserve, strictly protected and left undisturbed by human activities.
- It provides a habitat for diverse flora and fauna, safeguarding entire ecosystems.
- Ecosystems in the core zone remain in their natural state and serve as reference points for scientific research.
Buffer Zone: Balancing Nature and Human Interaction
- Surrounding the core zone, the buffer zone acts as a transition area where human activities are regulated to ensure harmony with nature.
- This zone also functions as a laboratory for scientists to study the natural environment and conduct research.
- Education and training initiatives often take place in the buffer zone, promoting sustainable practices.
Transition Zone: Coexistence of Culture and Ecology
- The outermost zone is the transition zone, where local communities reside and practice socio-culturally and ecologically sustainable activities.
- It provides opportunities for sustainable economic development, supporting livelihoods that respect environmental balance.
- These zones foster partnerships and collaborations among local communities, conservationists, and scientists.
Global Reach and Impact
- Globally, there are 748 designated Biosphere Reserves in 134 countries, with some being transboundary sites that promote cooperation between neighbouring nations.
- These reserves impact the lives of over 250 million people across 134 countries, illustrating their far-reaching influence.
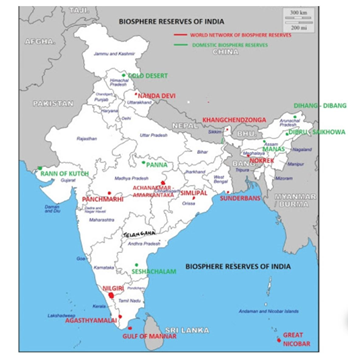
Biosphere Reserves in India
India boasts 18 Biosphere Reserves, designed to safeguard more extensive natural habitats than conventional national parks or wildlife sanctuaries. These reserves frequently encompass one or more national parks or reserves, in addition to buffer zones that permit certain economic activities.
Out of the total 18 biosphere reserves, 12 are affiliated with the World Network of Biosphere Reserves, as per the UNESCO Man and the Biosphere (MAB) Programme.
- Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve (Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka)
- Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve (Tamil Nadu)
- Sundarbans Biosphere Reserve (West Bengal)
- Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve (Uttarakhand)
- Nokrek Biosphere Reserve (Meghalaya)
- Panna Biosphere Reserve (Madhya Pradesh)
- Similipal Biosphere Reserve (Odisha)
- Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve (Andaman and Nicobar Islands)
- Achanakmar-Amarkantak Biosphere Reserve (Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh)
- Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve (Kerala, Tamil Nadu)
- Khangchendzonga Biosphere Reserve (Sikkim)
- Panna Biosphere Reserve (Madhya Pradesh)
- Manas Biosphere Reserve (Assam)
- Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve (Madhya Pradesh)
- Nokrek Biosphere Reserve (Meghalaya)
- Seshachalam Hills Biosphere Reserve (Andhra Pradesh)
- Dihang-Dibang Biosphere Reserve (Arunachal Pradesh)
- Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve (Himachal Pradesh)
Note: The Bold ones are affiliated with the World Network of Biosphere Reserves.
World Biosphere Reserve Day: Recognizing Their Significance
- Celebrated on November 3 each year to raise awareness about the importance of biosphere reserves.
- UNESCO designates biosphere reserves to promote biodiversity conservation, sustainable development, and research.
- Other United Nations agencies, including the United Nations Development Programme, the United Nations Environment Programme, and the International Union for Conservation of Nature, support these reserves.
The Vital Role of Biosphere Reserves
- Biosphere reserves are essential for the planet’s future, exemplifying nature’s resilience amid human activity.
- They house diverse ecosystems, from tropical rainforests to alpine deserts, providing shelter for countless unique and endangered plant and animal species.
- Beyond biodiversity protection and sustainable resource use, they offer opportunities for sustainable economic development.
- In recent years, they have become pivotal in the fight against climate change, housing many of the world’s carbon sinks that absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
- These carbon sinks, including forests and oceans, are crucial for implementing climate change adaptation strategies.
Local Conservation Efforts
- Biosphere reserves have witnessed substantial progress in conservation efforts at the local level.
- In the Sundarban Biosphere Reserve in India, local communities collaborate to manage mangrove forests and protect the region’s biodiversity.
- The Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve in India showcases the active participation of local communities, including women forming self-help groups and youth engaging in eco-tourism.
- Recently honoured with the UNESCO Michel Batisse Award for Biosphere Reserve Management 2023, the Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve Trust introduced the concept of “plastic checkpoints.”
- Community members inspect vehicles and tourists for plastic waste, which is then collected, recycled, and used for road construction.
- In times of global challenges such as climate change, biodiversity loss, and sustainable development, the role of biosphere reserves becomes even more vital.
Challenges and Threats
- Despite being crucial ecosystems protecting nature, biosphere reserves are not immune to threats such as deforestation, invasive species, and changes in land use like mining.
- With the world’s population continuously growing and urbanization on the rise, human exploitation is increasing.
The 10th South and Central Asian Biosphere Reserve Network Meeting
- UNESCO, in collaboration with India’s Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change, and the National Centre for Sustainable Coastal Management, concluded the 10th South and Central Asian Biosphere Reserve Network Meeting (SACAM) in Chennai, India from November 1 to 3.
- Themed “Ridge to Reef,” SACAM offered a platform for knowledge exchange and collaborations in sustainable environmental practices in the South and Central Asia Region.
- The UNESCO Man and the Biosphere (MAB) program combines natural and social sciences to enhance the human-environment relationship, improve livelihoods, safeguard ecosystems, and promote sustainable economic development.
Biosphere reserves exemplify the coexistence of nature and humanity, offering a beacon of hope in a world grappling with environmental challenges. They are an acknowledgment of the power of conservation, sustainable practices, and scientific research in nurturing our planet’s future. On the occasion of World Biosphere Reserve Day, let us recognize and safeguard these vital ecosystems that stand as living proof of our planet’s resilience.
Source: The Hindu
Mains Question
Discuss the significance and role of Biosphere Reserves as beacons of hope in the face of the climate crisis. Also, examine the challenges and threats faced by Biosphere Reserves.