In With the World
Inclusion in global indices will increase capital flows into India Relevance
GS Paper 3 Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
- Inclusive growth and issues arising from it.
- Tags: #JPmorgan #globalbonds #GBI-EM #India #currentaffairs #upsc.
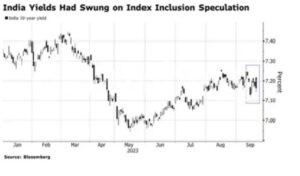
Why in the News?
India’s emergence as an attractive investment hub and global economic force is imminent, thanks to nearly a decade of meticulous government and regulatory efforts. A significant milestone in this journey is JP Morgan’s decision to include India in its Government Bond Index-Emerging Markets (GBI-EM) index, scheduled to commence on June 28, 2024.
Gradual Inclusion Process
- JP Morgan’s inclusion will span over 10 months, incrementally increasing India’s index weighting by 1 percent, ultimately reaching a maximum weighting of 10 percent.
- This move will encompass nearly two dozen Indian government bonds, collectively valued at $330 billion.
Anticipated Inflows
- Expectations suggest that total flows could reach a remarkable $45-50 billion within the first 12-15 months of India’s inclusion in the GBI-EM index, significantly surpassing the $40 billion received over the past decade.
- However, annual flows will depend on macroeconomic dynamics and the momentum of active and passive investments.
Beyond JP Morgan’s Index
- While India’s inclusion in JP Morgan’s GBI-EM index is a major achievement, it does not automatically guarantee inclusion in other influential global bond indices, such as the FTSE EM Index and the Bloomberg Barclays EM bond index.
- Stringent procedural requirements, operational hurdles, taxation clarity, and Euroclear participation remain crucial factors.
Implications of Inclusion
The inclusion of Indian government bonds in these benchmark bond indices carries several significant implications:
- Reduced Vulnerability to Global Capital Markets:India’s status as a substantial importer of global capital means its economic and business cycles are more susceptible to fluctuations in global capital markets, especially U.S. interest rates and the dollar.
- Financing Twin Deficits:Inclusion provides an alternate source of funds, easing the financing constraints on India’s fiscal and current account deficits. This structural shift will lower risk premia, reduce funding costs, deepen bond markets, and stabilize the exchange rate.
- Benefits for Corporates:A lower yield curve will lead to sustained lower financing costs for corporates. This will narrow corporate bond spreads and offer positive sentiments for the sector.
- Relief for Banking Sector:Reduced pressure on commercial banks to absorb government bonds will free up balance sheets for increased lending to the private sector, fostering economic growth.
- Infrastructure Investment:As India focuses on infrastructure development, bond inclusion offers a long-term and sustainable financing source through government securities investment.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the positive outlook, India’s inclusion in global indices comes with challenges and considerations:
- Increased scrutiny on government finances and fiscal responsibility.
- Rising crude oil pricesimpacting the fiscal outlook.
- Dependency on foreign fundsfor domestic deficits poses macroeconomic risks.
- Exposure to greater market volatilitythrough passive investment flows.
- Addressing operational hurdles such as international clearing, repatriation of funds, and tax complexities.
Incorporation into global bond indices represents a significant step forward for India’s financial markets. As reforms continue and market access becomes more accessible and transparent, India’s integration into global markets will pave the way for unparalleled market development, long-term capital inflows, and innovative financial products. However, it remains crucial to navigate challenges and maintain fiscal prudence as India’s economic journey unfolds.
| Global Bond Indices:
· These indices track local currency bonds issued by governments in developing nations. Prominent examples include JP Morgan and Bloomberg–Barclay’s indices. Significance: · Global bond indices aid investors by monitoring bond movements across jurisdictions and enabling relative comparisons. They serve as benchmarks for mutual funds and other long-term investors. Types: · Bond indices cover high-yield, emerging market, and government bonds. Criteria for Inclusion: · Market Size: A substantial bond market size is attractive. · Country Rating: Creditworthiness matters. · Access Ease: Investors should access and trade bonds easily. Country-Level Criteria: · Capital Flow: No capital restrictions. · Forex Availability: Adequate foreign exchange. · Hedging: Reliable currency risk mitigation. · Tax Laws: Investor-friendly tax regulations. · Trade Settlement: Efficient and secure processes. |
Sources: Indian Express.
Mains Question
“Discuss the socio-economic impact of India’s recent inclusion in global bond indices on its financial stability and economic growth prospects.” 250words.