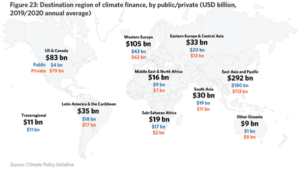
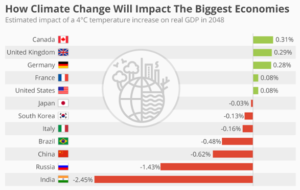
Move beyond greenwishing and greenwashing.
Relevance
- GS Paper 3 Conservation, Environmental Pollution and Degradation, Environmental Impact Assessment.
- Tags: #ClimateFinance #ClimateAction #GreenInvestment #ClimateResilience #COP28 #DigitalAssets #ETFs #ClimateChange #GreenTransition #UPSC #MintEditorial.
Why in the News?
As the urgency of addressing climate change intensifies, there is a growing need to move beyond mere aspirations and empty gestures. The upcoming CoP-28 provides a critical opportunity to reshape climate finance and harness innovation for meaningful impact.
Unlocking Private Sector Capital for Climate Action
As we transition from UN Climate Week to CoP-28 in Dubai later this year, it is crucial to move beyond mere “greenwishing” and “greenwashing.”
- Instead, we must focus on developing effective instruments that empower the private sector and private investors to direct more capital toward climate resilience and sustainable development.
- While the public sector plays a vital role, addressing climate challenges necessitates substantial private-sector commitments.
- Given the widespread impacts of climate change, mobilizing this largely untapped capital source has become mandatory.
Challenges in Climate-Centric Investments
- Some investors see climate-focused investments as less profitable and more about social impact.
- Sophisticated investors can profitably invest in climate sectors, but these investments are often illiquid.
- Ordinary investors and savers, most affected by climate risks, can’t easily access these investments.
- Impact on Food, Water, Energy: Climate-driven insecurity in these vital areas highlights the need for accessible investments.
Creating Profitable, Accessible Climate Investments
- CoP-28 Opportunity: CoP-28 provides a chance to reimagine market solutions for climate investments.
- Digital Innovation: Leveraging digital innovation can help scale up effective models.
- Mobilizing Capital: We need to tap into global savings from individual investors and institutions like pension funds, insurers, and sovereign funds.
- Risk Diversification: Retail-friendly, easily accessible instruments like exchange-traded funds (ETFs) can spread risks and make climate investments more accessible to all.
Building a Profitable, Climate-Aligned Investment Strategy
To create a profitable, long-term, and widely accessible investment strategy that supports climate financing, consider a diversified portfolio of assets. Such a portfolio should include three main asset types for investors
First- Investing in Climate-Resilient Real Estate and Infrastructure
- Climate-resilient assets are those located in stable regions with low climate risks
- They can experience significant value appreciation due to population shifts from high-risk areas in the Southern Hemisphere to more resilient zones like North America, Northern Eurasia, and select areas in the Global South.
Investment Options
- Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs): These carefully selected REITs can provide reliable returns by investing in climate-adapted properties.
- ETFs with Greenfield Developments: Investing in ETFs that focus on greenfield developments offers exposure to sustainable projects.
Benefits
- Profitability: The value of investments made in infrastructure and real estate that is climate resilient is expected to increase.
- Economic Growth: These investments contribute to broader economic growth.
- Job Creation: They create jobs and employment opportunities.
- Housing Solutions: They address housing needs for migrating populations.
Second- Investing in Green Commodities
- Transitioning to a resilient future demands significant investments in not only energy, food, and water but also crucial materials for renewable energy and electric vehicles (EVs).
- These materials include soy, wheat, copper, rare-earth elements, cobalt, lithium, and more.
Objectives
- Preventing Greenflation: Ensuring that efforts to decarbonize don’t lead to inflation.
- Avoiding Supply Shortages: Urgently increasing production and reducing costs to secure these vital commodities.
- Investing in green commodities is crucial to support sustainability efforts and prevent potential economic challenges like inflation and supply shortages.
Third – Inclusion of Hedge Assets
- Diversification for Resilience: A climate-aligned portfolio should incorporate assets that act as hedges against inflation and geo-economic risks.
Asset Types
- Sovereign Bonds: Including short-term and inflation-indexed sovereign bonds.
- Gold: A time-tested hedge against economic uncertainties.
Benefits
- Risk Mitigation: Negative correlation with climate-related investments enhances portfolio stability.
- Liquidity and Stability: Offers liquidity and low volatility suitable for individual investors, pensioners, and savers.
- Green Financing: Greater investments in inflation-proof sovereign assets can support government funding for green initiatives.
Inclusive Climate Investment Access
Climate-investment tools should be accessible to all, including average investors.
Challenges Faced
- Banking Limitations: Many individuals lack bank or brokerage accounts.
- Digital Generation: Younger generations and unbanked populations prefer digital assets.
- According to the World Bank, 1.4 billion adults globally lack banking access.
- Over 50% of unbanked individuals are found in select Middle Eastern, Asian, and African nations with sizable youth populations.
- Ensuring inclusive access to climate investments is essential, given the prevalence of unbanked individuals and the preferences of younger, digitally inclined generations.
Tokenized Climate Investments
- Climate investments should be digitally tokenized for global reach and safeguarding vulnerable populations.
- Backing with Real Assets: Digital assets must be backed by tangible physical and financial assets to be effective.
- Risk Mitigation: Ensuring liquidity and preventing speculation during crises is vital to prevent digital climate investments from becoming worthless crypto assets.
- Tokenizing climate investments digitally can offer wide accessibility while maintaining real-world asset backing, minimizing financial risks.
To foster climate resilience, policymakers and asset owners must rethink large-scale capital deployment, fostering global partnerships, securing green supplies, and accommodating climate-induced population shifts. Rapidly rising climate-related costs make innovation, technological and financial, important. As CoP-28 nears, there’s no room for delay or mere wishful thinking; decisive action is paramount.
Source: Livemint
Mains Question
What are the challenges associated with directing private-sector capital into climate resilience and sustainable development, and how can digital innovation and financial instruments like ETFs address these challenges?