Daily News Analysis.
NavIC in all Indian smartphones by 2025
News: All smartphones in India will be required to support the indigenous Navigation System, NavIC, by the end of 2025.
- Apple has already incorporated NavIC support in some of its new iPhone 15 models.
- 5G smartphones must support NavIC by January 1, 2025, while other phones have until December 2025 to comply.
- The government is considering offering incentives to encourage the use of Indian-made or -designed NavIC-supporting chips in smartphone system designs.
- These incentives could be similar to those provided under the IT hardware Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme, which rewards companies that source locally made components, including chips, for laptops, computers, and servers.
- The goal is to promote the use of NavIC in smartphones and create a competitive mobile phone grid chip designed or made in India.
NavIC- Navigation with Indian Constellation.
- An indigenous satellite-based navigation system developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- It is designed to provide accurate and reliable positioning and timing information over India and the surrounding region.
- NavIC is similar to other global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) like GPS (United States), GLONASS (Russia), Galileo (European Union), and BeiDou (China).
- The NavIC constellation consists of a group of seven satellites in geosynchronous and geostationary orbits.
- Valuable for a wide range of applications, including transportation, agriculture, disaster management, and defense.
PMMSY: bridging gaps in fisheries sector
News: India Ranks among Top Three Nations in Global Fish and Aquaculture Production.
- In 2020, Indian fisheries sector faced a potential setback due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi recognized the sector’s potential and allocated ₹20,050 crore for the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY).
- Aim: To address critical gaps in the fisheries value chain, focusing on fish production, productivity, quality, technology, infrastructure, and marketing.
- Key Priority Areas: Marine fisheries, inland fisheries, fishermen’s welfare, and post-harvest management.
- Impact: PMMSY empowered young entrepreneurs, especially women, to venture into fisheries and adopt innovative practices.
- It expanded fisheries to non-traditional areas and promoted aquaculture in landlocked regions.
- Initiative supported research, genetic improvement, and domestication of shrimp.
- India became a top global producer in fish and aquaculture, and the largest shrimp exporter.
- The government recently announced a ₹6,000 crore investment under PMMSY, totaling over ₹38,500 crore in fisheries development over nine years.
- Prime Minister Modi empowers fishing community with ‘Sabka Sath, Sabka Vikas, Sabka Vishwas, Sabka Prayas’ vision.
Bharat Granted Internationally Accepted OIML Certificates
News: Bharat joins 12 nations issuing Internationally Accepted OIML Certificates, achieving global recognition in legal metrology.
OIML Membership and Authority
- OIML (International Organization of Legal Metrology) established in 1955.
- Bharat became an OIML member in 1956.
- OIML comprises 63 Member States and 64 Corresponding Members.
- Bharat now holds authority to issue internationally accepted OIML certificates for weights and measures globally.
Compliance and Acceptance
- Bharat adheres to OIML recommendations and testing/calibration procedures for weights and measures.
- Bharat can issue OIML pattern approval certificates, supporting indigenous manufacturers and enabling cost-effective exports.
- This generates foreign exchange earnings for Bharat.
Influence and Policy Contribution
- Bharat’s authority allows it to influence OIML policies and contribute to the OIML Strategy.
- Bharat’s recognition as an OIML Certificates Issuing Authority reflects its commitment to quality standards and international trade facilitation.
International Trade Facilitation
- OIML certificates from Bharat can serve as the basis for national/regional type approvals worldwide.
- This reduces the need for expensive test facilities in other OIML Member States.
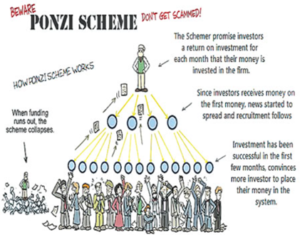
Ponzi scheme
News: Odisha Police’s Economic Offence Wing EOW may summon actor Govinda for alleged involvement in Ponzi scheme, causing investor losses.
- Ponzi Scheme term coined in 1919, named after Italian con-man Charles Ponzi, who arrived in the US in 1882.
- A fraudulent investment scheme where returns are paid to earlier investors using funds from newer investors rather than legitimate profits.
- Ponzi schemes promise high returns with no legitimate business, pay early investors to attract more, but are unsustainable without constant new investments.
- Notable Cases: Some high-profile Ponzi schemes in India include Saradha Group, Pearl Agrotech Corporation Limited, and Sahara India Real Estate Corporation Limited.
Legal Regulation
- In India, safeguards against Ponzi schemes are established through the Prize Chit and Money Circulation (Banning) Act, 1978, enforced by state governments.
- The Enforcement Directorate, under the Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002, also handles such cases.
- Additionally, the Banning of unregulated Deposit Schemes Act, 2019, imposes strict penalties, including imprisonment from 1 to 10 years and fines ranging from 2 lakh to 50 crore rupees.
- This act prioritizes depositors’ claims on recovered funds and ensures disgorgement of illegal deposits.
Non-partisan civil society aids Manipur’s peace
News: The ongoing ethnic violence in Manipur has raised concerns over the role of civil society representatives in promoting peace.
- Meira Paibi’s Involvement: The Meira Paibi, an organization of Meitei women, known for their activism against various issues, has been disrupting the operations of the Assam Rifles in the conflict areas, particularly in the “buffer zones” aimed at preventing further violence.
- Looting of Weapons: The situation has escalated due to the looting of weapons by different ethnic groups and their use in the ongoing strife.
- Challenges in Maintaining Peace: Both the State government and the Union government-deployed armed forces have faced challenges in maintaining peace, partly due to civil society groups supporting those engaged in violence.
- Disputing Buffer Zones: Some Meira Paibi representatives have even disputed the legality of the buffer zones, further complicating the situation.
- Role of Civil Society: Civil society groups like Meira Paibi have the potential to advocate for justice and reconciliation, but their involvement in promoting ethnic hatred has hindered progress.
- Need for Non-Partisan Leadership: History shows that achieving a breakthrough in such conflicts requires non-partisan leadership and civic dialogue among different stakeholders.
- Credible Alternative: To facilitate peace-building, there needs to be a credible alternative to the current leadership in the State that can bridge ethnic divides and promote reconciliation.
Civil Society
- Civil society refers to organizations and individuals outside of government and business sectors who work collectively for social, political, and environmental causes.
- Examples: Amnesty International, PUCL (People’s Union for Civil Liberties)
Government tests emergency alert system
News: Government conducted nationwide test of emergency alert system, sending messages to smartphones for disaster preparedness.
- The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) conducted a pan-India test of its emergency alert system today to evaluate its effectiveness and address potential issues.
- People received flash messages on their smartphones as part of this test.
- The NDMA intends to conduct similar tests in different regions periodically as part of its disaster management preparedness efforts.
National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA)
- Formation: NDMA was established in 2005, following the enactment of the Disaster Management Act, 2005.
- Mandate: It’s the apex body responsible for formulating policies, plans, and guidelines for disaster management in India.
- Chairperson: The Prime Minister of India serves as the ex-officio chairperson, emphasizing the highest level of political commitment to disaster management.
- State-Level Bodies: Every state in India has a State Disaster Management Authority (SDMA) and a District Disaster Management Authority (DDMA) to implement NDMA’s policies at the grassroots level.
Functions
- Formulating National Disaster Management Plans.
- Laying down policies, guidelines, and best practices for disaster management.
- Capacity building and training for disaster response.
- Promoting research and development in disaster management.
- Coordinating disaster response and relief efforts.
- Advising the Central Government on disaster-related matters.
India’s Permanent representative to United Nations Ruchira Kamboj says peace has always been important part of India rich cultural & philosophical heritage
News: According to Ruchira Kamboj, India’s permanent representative to the UN, peace has always played a significant role in India’s rich philosophical and cultural legacy. She made her statement yesterday at the Discourse on Peace conference in New York.
- She claimed that the nation’s approach to resolving disputes has been influenced by Mahatma Gandhi’s principles of nonviolent resistance.
- When discussing India’s assistance to the Global South, she emphasized that the country’s $ 40 billion development projects with the region show an unchanging dedication to a human-centered world.
Relevance of India’s rich culture and heritage
- India’s cultural diversity serves as a source of national unity and pride. Its myriad languages, religions, and traditions are a testament to the country’s ability to harmoniously accommodate differences, fostering a sense of unity in diversity.
- India’s cultural heritage is a global treasure trove of knowledge and wisdom. From ancient texts like the Vedas and Upanishads to the timeless teachings of Mahatma Gandhi, India’s intellectual contributions have influenced the world.
- Yoga and Ayurveda, for instance, have gained global recognition for their holistic health benefits. India’s vibrant arts, including music, dance, and literature, continue to captivate audiences worldwide.
- India’s historical monuments and architectural wonders, such as the Taj Mahal and Jaipur’s palaces, attract tourists and serve as a symbol of the country’s glorious past.
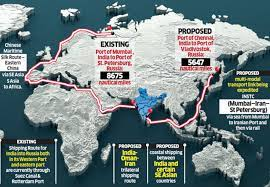
Eastern Maritime Corridor
News: The Eastern Maritime Corridor is a strategic and economically significant development initiative in India, aimed at bolstering maritime trade, connectivity, and overall economic growth along the eastern coast of the country.
Geographical aspects of the corridor
- Spanning from the northern state of West Bengal to the southern state of Tamil Nadu, this corridor encompasses a wide range of ports, infrastructure projects, and transportation networks.
- At the heart of the Eastern Maritime Corridor are the major ports such as Kolkata (West Bengal), Paradip (Odisha), Visakhapatnam (Andhra Pradesh), Chennai (Tamil Nadu), and several minor ports.
- These ports have been modernized and expanded to handle larger cargo volumes, making them key drivers of international trade.
Infrastructural developments
- The corridor involves the development of efficient transportation infrastructure, including highways, rail networks, and inland waterways.
- This integration of transportation modes allows for the smooth movement of goods to and from the ports, reducing logistics costs and enhancing trade.
- The Eastern Maritime Corridor is expected to stimulate economic growth in the region by attracting investments and fostering industrial development along the coastline.
- It not only facilitates exports but also encourages import-dependent industries to set up operations in the vicinity of these ports.
- The Eastern Maritime Corridor also seeks to strengthen connectivity with neighboring countries like Bangladesh, Myanmar, and Thailand through initiatives like the Kaladan Multimodal Transit Transport Project.
Strategic significance
- It enhances India’s maritime capabilities, making it better equipped to handle geopolitical challenges in the Indian Ocean region.
- It reduces dependence on a single corridor (the Western coast) for maritime trade, thus enhancing India’s maritime resilience.
- Environmental impact assessments and mitigation measures are incorporated into the planning and execution of projects to protect fragile coastal ecosystems.
- The development of ports and associated industries along the Eastern Maritime Corridor generates employment opportunities, both directly and indirectly, contributing to the socio-economic development of the region.
In conclusion, the Eastern Maritime Corridor is a transformative initiative that holds the potential to reshape India’s economic and strategic landscape. By bolstering maritime infrastructure and connectivity along the eastern coast, it not only fosters economic growth but also strengthens India’s position in the global maritime arena while promoting sustainable development and regional cooperation.
K2-18b Exoplanet
News: K2-18b is an exoplanet that has garnered significant attention in the field of astronomy due to its unique characteristics, including its potential habitability. Located approximately 124 light-years away from Earth in the constellation Leo, K2-18b was discovered in 2015 using data from the Kepler Space Telescope.
Key features
- K2-18b is classified as a “super-Earth” exoplanet, which means it is larger and more massive than Earth but smaller than gas giants like Neptune. It has a radius about 2.7 times that of Earth.
- One of the most intriguing aspects of K2-18b is its location within the habitable zone of its parent star, K2-18. The habitable zone, also known as the “Goldilocks zone,” is the region around a star where conditions might be right for liquid water to exist on the surface, a crucial factor for potential habitability.
- Researchers have used spectroscopic data to analyze K2-18b’s atmosphere, revealing the presence of water vapor.
- The detection of water vapor is significant because it suggests the possibility of a climate that could support life as we know it.
- While K2-18b is larger than Earth, its exact composition remains a subject of debate. It could be a rocky planet with a substantial atmosphere, including hydrogen and helium, or it might possess a more significant fraction of volatiles and gasses.
Challenges
- It orbits a red dwarf star, which tends to emit more radiation in the form of flares compared to Sun-like stars. These flares could impact the planet’s atmosphere and surface conditions.
Future Exploration
- K2-18b has sparked interest among astronomers, and future missions, such as the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), will play a crucial role in studying its atmosphere in more detail.
- The JWST will be able to analyze the exoplanet’s atmosphere for signs of key chemicals and potentially habitable conditions.
FDI in pharmaceutical sectors
News: Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in the pharmaceutical sector is a significant driver of growth and innovation in the global pharmaceutical industry. FDI refers to the investment made by foreign entities, such as multinational pharmaceutical companies or investors, into the pharmaceutical sector of a host country.
Key points
- The pharmaceutical industry is one of the largest and most important sectors globally, responsible for the development, production, and distribution of drugs and medications.
- FDI in this sector allows countries to tap into this lucrative market and benefit from international collaborations.
- FDI often brings with it advanced research and development Foreign pharmaceutical companies may establish research centers or partner with local institutions to develop new drugs and technologies.
- This contributes to scientific advancements and the creation of innovative medicines.
- FDI can facilitate the transfer of advanced manufacturing technologies and practices to the host country. This can lead to improved production efficiency, product quality, and compliance with international standards.
- Investment in the pharmaceutical sector creates job opportunities, both directly and indirectly like hiring scientists, researchers, production workers, and support staff.
- Additionally, the supply chain, including suppliers and distributors, benefits from increased economic activity.
- Host countries that attract FDI in pharmaceuticals often gain easier access to international markets which is advantageous for developing countries looking to expand their pharmaceutical exports.
- FDI in pharmaceuticals often involves navigating complex regulatory landscapes, as drugs must meet stringent safety and efficacy standards.
- FDI can contribute to the improvement of healthcare systems in host countries by providing access to a wider range of medications and therapies, fostering competition, and potentially lowering healthcare costs.
Challenges
- FDI in pharmaceuticals sometimes raises concerns about intellectual property rights. Host countries must balance the need for innovation with the necessity of affordable access to medications.
- Sustainability and ethical practices in pharmaceutical manufacturing are increasingly important.
- Host countries and foreign investors should collaborate to ensure environmentally responsible and ethically sound pharmaceutical production.
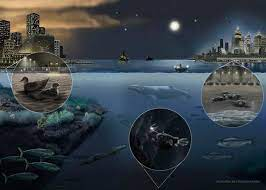
Marine light pollution threatens the coastal ecosystem
News: Marine light pollution, often referred to as “coastal light pollution,” poses a significant threat to coastal ecosystems worldwide. This phenomenon occurs when artificial light from coastal cities and development disrupts the natural darkness of coastal areas.
Ways how marine light pollution affects these delicate ecosystems
- Many marine species, including sea turtles, seabirds, and various fish, rely on natural light cues from the moon and stars to navigate and carry out crucial activities like feeding and reproduction.
- Artificial light interferes with these natural behaviors, leading to disorientation and making it difficult for these animals to find food or suitable nesting sites.
- Sea turtles, in particular, are highly affected by coastal light pollution. Hatchlings are attracted to artificial lights instead of the moon’s reflection on the ocean, leading them away from the water and toward dangerous urban areas.
- Predatory species that hunt at night, such as owls and certain fish, have difficulty finding prey when coastal areas are illuminated. This disrupts the natural balance of coastal food webs and can lead to population declines among these species.
- Coral reefs, vital marine ecosystems, are also affected by light pollution. The excessive artificial light can disrupt the circadian rhythms of coral, impacting their health and growth.
- This, in turn, affects the entire reef ecosystem, including the numerous species that rely on coral reefs for shelter and food.
- Coastal areas often serve as crucial stopover points for migratory birds during their long journeys. Light pollution can disorient these birds, causing them to collide with buildings and other structures, leading to injuries and deaths.
- Marine organisms that rely on specific light cues for activities like spawning or bioluminescence may have their natural behaviors disrupted.
- For example, excessive light pollution can interfere with the mesmerizing spectacle of bioluminescent plankton, a phenomenon enjoyed by tourists in some coastal areas.
- The disruption caused by marine light pollution can create imbalances in coastal ecosystems, leading to declines in certain species and the proliferation of others. This can have cascading effects throughout the ecosystem.
Engineers’ Day
News: Engineers’ Day in India is celebrated on September 15th every year to commemorate the birth anniversary of one of the country’s most eminent engineers, Sir Mokshagundam Visvesvaraya. This day is a tribute to his contributions to the field of engineering and his role in shaping modern India.

Sir M. Visvesvaraya
- Sir M. Visvesvaraya, often affectionately referred to as “Sir MV,” was born on September 15, 1861, in Muddenahalli, Karnataka.
- He was an exceptional civil engineer, statesman, and visionary who played a pivotal role in India’s infrastructure development during the early 20th century.
Remarkable Contributions
- KRS Dam One of his most celebrated achievements is the construction of the Krishna Raja Sagara Dam (KRS Dam) in Mandya, Karnataka. This dam, built across the river Cauvery, revolutionized irrigation practices in the region and helped in mitigating droughts.
- As the Chief Engineer of Mysore State, Sir MV implemented various innovative irrigation and flood control techniques, transforming Mysore into a model state for development and water management.
- Sir MV emphasized the importance of industrialization for India’s economic growth. He played a significant role in establishing several industries and factories in India, fostering economic self-sufficiency.
- Sir MV was instrumental in the founding of the Government Engineering College in Bangalore (now known as Visvesvaraya Technological University), which has since become a premier institution for engineering education in India.
- In recognition of his outstanding contributions, Sir MV was awarded the Bharat Ratna, India’s highest civilian honor, in 1955.
E-Courts Mission Phase III
News: E-Courts Mission Mode Project Phase III is a significant initiative undertaken by the Government of India to modernize the Indian judiciary and enhance access to justice through the use of technology. This project builds upon the success of the earlier phases and aims to further digitize and streamline court processes across the country.
Key aspects and Objectives
- Phase III focuses on the comprehensive digitization of court processes, including case filings, case management, and case disposal.
- It aims to reduce paperwork, increase transparency, and enhance the efficiency of court proceedings.
- The project aims to expand and improve the NJDG, which is a central repository of case data from across the country.
- This allows for better monitoring of case status and pendency, enabling data-driven decision-making.
- E-Courts Phase III emphasizes interoperability, ensuring that different components of the justice system can communicate and share data seamlessly. This promotes consistency and efficiency in the handling of cases.
- The project seeks to integrate with other critical systems, such as police, prisons, and legal aid services, to create a more holistic and efficient justice ecosystem.
- It encourages the adoption of e-filing and e-payment systems, making it easier for litigants to file cases and pay fees online. This reduces the need for physical visits to the courts and simplifies administrative tasks.
- E-Courts Phase III includes extensive training programs to familiarize judges, lawyers, and court staff with the new technologies and processes.
- By enhancing the efficiency and transparency of the judicial system, the project aims to improve access to justice for all citizens, particularly those in remote or underserved areas.
- Robust security measures are put in place to protect sensitive case data and maintain the confidentiality and privacy of individuals involved in legal proceedings.
- The project includes mechanisms for monitoring and evaluating its progress and impact, allowing for adjustments and improvements as needed.