New licensing policy to boost drug safety.
Relevance
- GS Paper 2 Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- Tags: #pharma #drugs #cdsco #WHO #currentaffairs #upsc.
Why in the News?
The health ministry has shared the draft with the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) for input.
The Union health ministry is set to introduce significant changes to its drug licensing program in an effort to establish consistency across India and enhance drug safety. This move comes in response to concerns that domestically produced cough syrups may have been linked to the deaths of children abroad. Here, we delve into the key aspects of this proposal.
Government Expert Panel’s Recommendation for Uniform Drug Approval Processes
Ensuring Consistency in Quality and Safety
- A government-appointed expert panel has stressed the importance of uniform implementation of documentation and dossier-based approval processes for drugs manufactured in India.
- This recommendation aims to ensure consistent quality and safety standards. The health ministry has taken steps to engage the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) for input on this crucial initiative.
Challenges Stemming from Lack of Uniformity
Inadequate Enforcement, Testing Infrastructure, and Competence
- Challenges include poor enforcement of regulations, insufficient development of testing infrastructure, and disparities in the competence of regulatory officials. One of the main contributors to this lack of uniformity is the issuance of drug manufacturing licenses by both the central government and individual states.
Concerns Regarding India’s Reputation as a Drug Supplier
- Indian health officials are concerned that contaminated medicines could severely damage the country’s reputation as a global supplier of pharmaceuticals.
- This concern follows the World Health Organization’s discovery that cough syrups made in India contained toxins linked to the deaths of children in The Gambia. India, however, has denied any connection between the syrups and the deaths.
Ensuring Safe and Quality Drugs
- Bringing uniformity to the drug regulatory mechanism is expected to result in safer, more effective, and higher-quality drugs. It will also ensure that pharmaceutical companies, especially smaller ones, adhere rigorously to Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines,
- The health ministry believes that uniform implementation of the provisions of the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940, will play a pivotal role in ensuring drug quality and safety.
Drugs Controller General of India’s Advisory
- The Drugs Controller General of India is advising state authorities to adopt document-based licensing nationwide. Simultaneously, the government is working to establish consistency in enforcement through risk-based inspections at manufacturing sites.
Uniform Inspection and Market Surveillance
- Efforts are underway to standardize inspections of manufacturing sites to ensure better drug quality and compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
- This involves assessing what needs to be inspected, considering previous inspection history, evaluating associated risks, reviewing past findings, and sampling procedures for sub-standard drugs.
- The plan also involves achieving uniform implementation of market surveillance for monitoring the quality of medicines in the supply chain. In India, over 100,000 drug samples are tested annually.
- However, the lack of a centralized database and uniformity in market surveillance processes has sometimes led to delays in investigations and prosecutions. The goal is to streamline the entire drug regulatory system.
| The Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO)
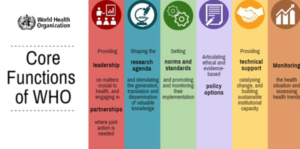
· It is India’s primary regulatory body for drugs and cosmetics. It operates under the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare and oversees drug approvals, clinical trials, quality standards, and coordination with State Drug Control Organizations. CDSCO, in collaboration with state regulators, grants licenses for critical drugs like vaccines. · The Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI) heads CDSCO and is responsible for approving licenses for specific drug categories and setting standards for drug manufacturing, sales, import, and distribution across India. The Indian government plans to subject all medical devices, including implants and contraceptives, to CDSCO scrutiny. The Drugs and Cosmetics Rules 1945 · It constitute the regulatory framework. · These rules encompass drug classification across specific schedules. · Provide comprehensive guidance on the storage, sale, display, and prescription of drugs within each schedule. World Health Organisation · The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) that is responsible for international public health. It was founded in 1948 with the aim of achieving “the highest attainable standard of health for all people”. · The WHO has 194 member states and is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland. It is governed by the World Health Assembly, which is the decision-making body of the WHO. The WHO’s main functions include 1. Providing leadership on global health matters 2. Setting norms and standards 3. Articulating evidence-based policy options 4. Providing technical support to countries 5. Monitoring and assessing health trends The WHO is involved in a wide range of activities, including · Disease prevention and control · Health promotion · Nutrition · Maternal and child health · Mental health · Noncommunicable diseases · Communicable diseases Health emergencies · The WHO plays an important role in global health governance. It is the leading international organization for public health and coordinates the work of other organizations and agencies in this area specially in times of epidemics and pandemics. · The WHO is a valuable source of information on global health. It publishes a wide range of reports, data, and guidelines on a variety of health topics. · The WHO is also involved in capacity building and training. It provides training to health workers and policymakers in developing countries. · The WHO is a key player in the global response to health emergencies. It coordinates the work of countries and other organizations to respond to outbreaks and pandemics. |
Sources: LiveMint.
Mains Question
“Discuss the significance of the proposed sweeping changes to India’s drug licensing program by the Union health ministry in ensuring drug safety and quality. Analyze the challenges arising from the lack of uniformity in drug regulations and highlight the potential impact on India’s reputation as a global pharmaceutical supplier. ” 250words.