Green Finance.
Relevance
- GS Paper 3 Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment.
- Tags: #greenfinance #climatechange #india #currentaffairs #upsc.
Why in the News?
- Climate finance and Green finance, remains critical bottleneck for India in its journey towards the Net Zero 2070 objective as reassured by PM Modi.
- In recent years, industries like power and steel have come under intense scrutiny for their significant contributions to the climate crisis.
- The urgent challenge of climate change demands a concerted effort to compel industries and businesses to adopt practices that mitigate their carbon footprint.
- Achieving this transformation requires substantial investment, and the solution lies in the concept of green financing.
What is Green Finance
- Green finance, according to the United Nations Environment Programme, involves increasing financial flows from various sectors, including banking, micro-credit, insurance, and investment, towards sustainable development priorities.
- A pivotal aspect of green financing is the enhanced management of environmental and social risks, seizing opportunities that yield both respectable returns and environmental benefits, and ensuring greater accountability.
Promoting Green Finance
- Several strategies can be employed to promote green finance. These include revising regulatory frameworks within countries, aligning public financial incentives with sustainability goals, encouraging increased green financing from diverse sectors, integrating the environmental dimension of the Sustainable
- Development Goals into public sector financing decisions, boosting investments in clean and green technologies, supporting financing for sustainable natural resource-based green economies and climate-smart blue economies, and fostering greater use of green bonds, among others.
Why Green Finance
- India has taken significant steps to address its carbon emissions and adapt to the impacts of climate change through updated Nationally Determined Contributions.
- This ambitious climate action plan aims to reduce the country’s carbon intensity by more than 45% by 2030, compared to 2005 levels.
- To achieve these renewable energy targets, India will require substantial financial resources. According to estimates by the International Finance Corporation, India will need approximately $403 billion in renewable finance by 2030.
- In this context, green finance emerges as a crucial instrument to secure the necessary funds and drive the transition towards a sustainable and environmentally responsible future.
Types of Green Financing
Green Mortgages
- Offer favorable terms to home buyers of environmentally sustainable properties.
- Support property buyers willing to invest in improving a property’s environmental performance.
Green Loans
- Fund environmental projects like household solar installations, electric vehicles, and energy efficiency upgrades.
Green Credit Cards
- Examples like Aspirations’ Zero card.
- Plant trees with each customer purchase.
- Empower consumers to contribute to green finance through everyday spending.
Green Banks
- Operate like traditional banks.
- Utilize public funds to stimulate private investments in renewable energy and eco-friendly initiatives.
- A significant growth observed in the number of green banks in the US from 2011 to 2020, investing $7 billion in renewable energy.
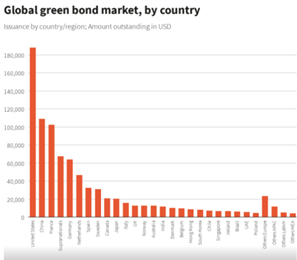
Green Bonds
- Predominant form of green financing.
- Involves bond investments with proceeds directed toward various green projects, including renewable energy, sustainable transportation, and conservation efforts.
India’s Sovereign Green Bonds: A Catalyst for Green Finance
- In a significant move, the Indian government is proactively championing green finance.
- A total of ₹25,000 crore worth of projects have been earmarked for funding through sovereign green bonds in the current fiscal year and the next.
- These projects are primarily centered around renewable energy and clean transportation initiatives.
- Initially, the government aimed to raise ₹16,000 crore through green bonds in two equal tranches during the current fiscal year.
- The first tranche, India’s debut issuance of sovereign green bonds in January, witnessed overwhelming demand.
- Orders surpassed the offer size of ₹8,000 crore by more than fourfold, highlighting investor enthusiasm.
Benefits of Green Finance
Encourages Spread of Technologies and Environmentally Friendly Infrastructure
- Governments in developing nations invest in infrastructure that promotes efficient resource management, enhances competitiveness, and attracts private sector investments in local green markets.
Produces a Comparative Advantage
- As environmental challenges become more pressing, transitioning to low-carbon green development can shift from being voluntary to mandatory.
- Embracing green financing early can provide a competitive edge when environmental regulations become stricter.
Adds Business Value
- Companies can bolster the value of their portfolios by actively participating in green financing.
- This demonstrates a commitment to sustainability, attracting environmentally conscious investors and customers.
Enhances Economic Prospects
- Governments supporting green financing initiatives contribute to resource sustainability.
- They foster local markets for renewable energy and explore new employment-rich markets, safeguarding their societies against resource scarcity.
Risks in Green Finance
Misuse and Lack of Regulation
- Green finance, being relatively new, carries the risk of potential misuse.
- Effective regulation is essential to prevent non-compliance and unscrupulous practices, ensuring the sector’s integrity.
Compliance and Governance Challenges
- Maintaining checks and balances early on is crucial to achieving compliance with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) standards.
- Ensuring good governance practices can safeguard a company’s reputation and goodwill.
Regulatory Uncertainty
- The absence of clear regulations can create uncertainty within the green finance sector.
- Regulatory frameworks are essential for promoting stable and consistent growth.
Climate Change-Related Risks
- Green finance is exposed to risks associated with climate change.
- Financial institutions must assess and mitigate climate-related risks in their lending and investment activities.
Market Volatility
- Green finance markets can be susceptible to fluctuations.
- Sudden shifts in investor sentiment or policy changes may impact the stability of green finance investments.
Green Finance vs. Sustainable Finance
Different Focus
- Green Finance: Concentrates solely on environmental objectives, such as reducing carbon emissions.
- Sustainable Finance: Encompasses broader environmental and social goals alongside financial considerations.
Green Finance in Banking Sector
- The banking sector is increasingly recognizing the importance of green finance.
- Initiatives involve integrating environmental factors into bank strategies, governance, and supporting green assets through various financial products, including green bonds.
- Global efforts, such as the Principles for Responsible Banking and the Sustainable Banking Network, are driving this transformation.
- MDBs play a crucial role in mobilizing international climate funding and enhancing financial support for low-carbon and climate-resilient projects.
- They focus on strengthening investment planning, financing, and risk mitigation, while also considering natural and social impacts.
Green and sustainable finance are reshaping the financial sector, attracting trillions in investments worldwide. Emissions from funded activities have a significant impact on carbon footprints, underscoring the importance of green financing, including investments, loans, and credit cards, in emission reduction. Banks are integrating environmental considerations into their strategies and products, influenced by initiatives like the Principles for Responsible Banking.
Sources: Economic Times, UNEP.
Mains Question
“To what extent is green financing integral to the attainment of the Net Zero target, and how has India endeavored to secure financial support for its climate action objectives?” 250words.