Preliminary Pointers
India’s first Solar City
- News: The country’s first solar city will be opened today in Sanchi, Madhya Pradesh.
- Benefits of such initiatives:
- Sanchi Solar City will cut carbon dioxide emissions by approximately 13 thousand 747 tonnes per year, which is comparable to more than 2 lakh adult trees. Along with this, the government and the people will save more than 7 crore rupees yearly on energy-related expenses.
- Solar energy will meet Sanchi’s power needs for the next five years as the city builds a solar city and becomes self-sufficient in power supply.
- Features of a solar city: There will be solar-powered street lights, garden lights, stud lights, high-mast lights, drinking water kiosks powered by the sun, battery-powered e-rickshaws for public transportation, charging stations, wind turbines powered by renewable energy and piezoelectric generators.
- Why Sanchi was selected ?
- Sanchi sees a huge number of tourists because of its distinctiveness and historical background and addition of solar power will promote the Sanchi in totality.
- A World Heritage Site is Sanchi as declared by UNESCO;
- Note: Government of India has set a goal of constructing a solar city in each state by 2070.
Why is Sanchi a historical figure?
What does a stupa serve as?
|
Black sea grain deal
- News: Russian President Vladimir Putin refuses to restore the Black Sea Grain deal.
About Black sea grain deal:
- Background of the deal:
- In addition to being a significant contributor to the UN’s food aid programmes, Ukraine is also one of the top exporters of cereals like wheat and maize in the world and Russia’s invasion and embargo on Ukraine have caused food prices to spike and sparked worries regarding food security in the world’s poorer countries.
- In light of this, the UN and Turkey succeeded in persuading Russia to support the Black Sea Grain Initiative.
- Actual deal between Russia and ukraine:
- Russia and Ukraine inked an agreement in July 2022 to restore grain shipments from Ukrainian Black Sea ports. The Black Sea Initiative is another name for the accord.
- After being inspected to ensure they weren’t carrying weapons, cargo ships would be permitted to depart from and arrive at the three Ukrainian ports of Odesa, Chornomorsk, and Pivdennyi (Yuzhny).
- The Black Sea’s safe route was three nautical miles broad and 310 nautical miles long.
- To manage and oversee the procedure, a control centre was constructed in Istanbul and staffed by U.N., Turkish, Russian, and Ukrainian officials.
- The agreement, which has been extended twice, expired on July 17, 2023.
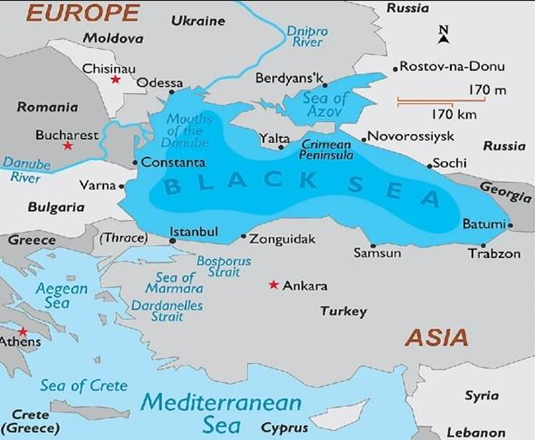
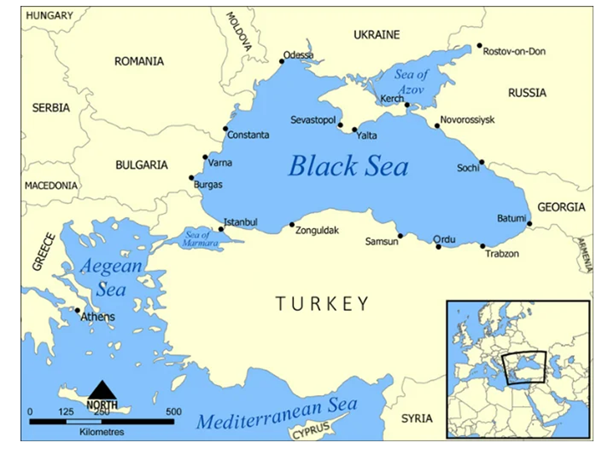
- About Black sea:
- The Black Sea, also known as the Euxine Sea, is a huge body of water and a well-known inland sea in the world.
- The Strait of Kerch connects the Black Sea to the Sea of Azov.
- The well-known body of water is bounded by:
-
-
- To the north and northwest is Ukraine.
-
-
-
- In the north, Crimea
-
-
-
- To the east, Russia and Georgia
-
-
-
- To the south, Turkey, and
-
To the west are Bulgaria and Romania, which connect to the Sea of Marmara via the Bosphorus and then to the Aegean via the Dardanelles
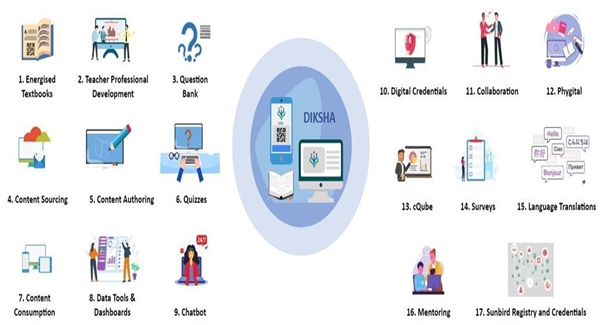
DIKSHA e-education platform
- News: Centre’s DIKSHA e-education platform to offer AI help.
- About:
- The Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing (DIKSHA) platform now used by India’s National e-Governance Division (NeGD) of the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) will be incorporating Personalised Adaptive Learning (PAL).
- PAL is a software-based methodology that attempts to give each student a customised educational experience based on their particular needs and skills.
- It is to be noted that the ministry is also including voice commands in DIKSHA 2.0 as part of AI-enabled learning. This would enable students to use voice commands to obtain chapter summaries and other content, much like ChatGPT.
- How integration will help students?
- The platform is anticipated to undergo a transformation with the integration of PAL into DIKSHA by employing artificial intelligence (AI) to meet the unique learning requirements of students.
- For example: If a Class 9 student is studying algebra and makes a calculation error, the AI learning system flags the error and loops the student back to a simple video explaining how to make the calculation.
DIKSHA
o DIKSHA (Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing) is an Indian national digital platform for school education. o The National Council for Educational Research and Training (NCERT), a division of the Indian government’s Ministry of Education, is the organization in in charge of it. o DIKSHA, which was introduced back in 2017 by the then M. Venkaiah Naidu, Vice President of India, and since then it has been widely adopted by all states, union territories, and central autonomous bodies/boards, including CBSE.
a. In order to fulfil the content requirements of NCERT, CBSE, and other states, DIKSHA offers a comprehensive collection of digital content that has been donated by schools, individual instructors, content partners, NGOs, and corporations under CSR. b. In order to assist children with special needs (CWSN), DIKSHA provides a wide array of materials, such as audio books, videos in Indian Sign Language (ISL), and dictionaries. c. Various teacher professional development initiatives, such as NISHTHA (National Initiatives for School Heads and Teachers Holistic Advancement) at various grade levels, are also housed on the platform. d. Through PM eVIDYA DTH-TV channels that are connected to DIKSHA by QR codes, NCERT provides content to students on a 24/7 basis, ensuring accessible from any location at any time. |
Global fintech fest (GFF)
- News: Fourth GFF is being hosted on September 5 to 7, 2023, at the Jio World Convention Centre, Mumbai.
- About GFF:
- The Global Fintech Fest (GFF), now in its fourth year, is expected to become the largest fintech thought leadership platform worldwide.
-
- The GFF acts as a dynamic forum each year to bring together policymakers, regulators, industry pioneers, academics, and important fintech stakeholders.
- Benefits of GFF: This convergence makes it possible for ideas to be shared, insights to be gained, and creativity to be stimulated. Today, GFF is the pinnacle of global fintech convergence.
- Organised by: The fourth Global Fintech Fest (GFF23) is being organised by the “National Payments Corporation of India” (NPCI), “Payment Council of India” (PCI), and “Fintech Convergence Council” (FCC).
- Theme: The theme of GFF23 is “Global Collaboration for a Responsible Financial Ecosystem – Inclusive | Resilient | Sustainable,” which is precisely integrated with Indian and international aspirations for inclusive and sustainable progress.
- The GFF is being supported by: The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, the Government of India, the Department of Economic Affairs, the Ministry of Finance, the Reserve Bank of India, the International Financial Services Centre Authority, as well as other international and Indian nodal organisations like The World Bank, RBIH, ONDC, CGAP, Knomad, Startup India, Invest India, MSC, and BTCA, among others, are all supporting the festival.
Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI)
- News: Two senior GAIL officials among five arrested in ‘Rs 50 lakh bribery case’.
- About CBI:
- Historical background: In order to look into allegations of corruption in the War and Supply Department, the colonial administration considered it necessary to establish the CBI during World War II. A statute was passed in 1941. In 1946, it was renamed the DSPE Act. A government of India resolution of April 1, 1963, issued by the Ministry of Home Affairs, established the CBI and became India’s top investigating police organization.
NOTE: The CBI is not a statutory entity but rather derives its authority to investigate from the Delhi Special Police Establishment Act of 1946.
- Historical background: In order to look into allegations of corruption in the War and Supply Department, the colonial administration considered it necessary to establish the CBI during World War II. A statute was passed in 1941. In 1946, it was renamed the DSPE Act. A government of India resolution of April 1, 1963, issued by the Ministry of Home Affairs, established the CBI and became India’s top investigating police organization.
Ministry responsible:
-
- The Department of Personnel, Ministry of Personnel, Pension & Public Grievances, Government of India, which is a division of the prime minister’s office, is in charge of overseeing its operations.
- However, the Central Vigilance Commission is in charge of overseeing investigations into violations under the Prevention of Corruption Act and it
- works in sync with the Lokpal and the Central Vigilance Commission.
Relevant facts:
-
- Additionally, it is the primary police organization in India that organizes inquiries on behalf of Interpol Member nations.
- It is similar to the finest investigation organizations in the world in terms of conviction rates, which can reach 65 to 70%.
- Note: The CBI is exempt from the scope of the Right to Information (RTI) Act.
Jurisdiction of CBI:
-
- On the recommendation of the concerned state government, the central government is permitted by Section 6 of the DPSE Act to ask the CBI to investigate a case falling under the purview of any state.
- The courts have the authority to request a CBI investigation and even to keep track of its development.
- The CBI can only investigate crimes in Union Territories on its own.
- CBI Director Appointment: According to the Lokpal Act of 2013, the Chief Justice of India, the Leader of the Opposition in the Lok Sabha, and a judge of the Supreme Court that he nominated would serve on the committee that recommended the CBI director’s appointment.