Financial Inclusion drives Equitable Growth
Relevance
- GS 3: Indian Economy and issues relating to Planning, Mobilization of Resources, Growth, Development and Employment.
- Tags: #FinancialInclusion #B20Summit #Mint #EditorialAnalysis #UPSC
Why in the News?
Financial inclusion, a global policy tool to reduce poverty and inequality, has been a key focus at B20 summits. Despite progress, challenges remain in reaching underserved groups and closing the gender gap.
Advancing Financial Inclusion through Global Policymaking
- Financial inclusion is a vital tool employed by policymakers worldwide to combat poverty, reduce inequality, boost livelihoods for marginalized populations, and stimulate global economic growth.
- This initiative has been integral to B20 discussions for a significant period.
Milestones in Financial Inclusion at B20
- Pittsburg Summit (2009): Establishment of the Financial Inclusion Experts Group (FIEG).
- Seoul Summit (2011): Formation of the Global Partnership for Financial Inclusion (GPFI).
- Mexico Summit (2012): Introduction of fundamental financial inclusion indicators.
- China Summit (2016): Adoption of high-level principles for digital financial inclusion.
- Indonesia Summit (2022): Provision of an implementation guide.
Progress and Ongoing Challenges
- Although the B20’s efforts have resulted in notable advancements, there is still a long way to go until financial inclusion is fully advanced.
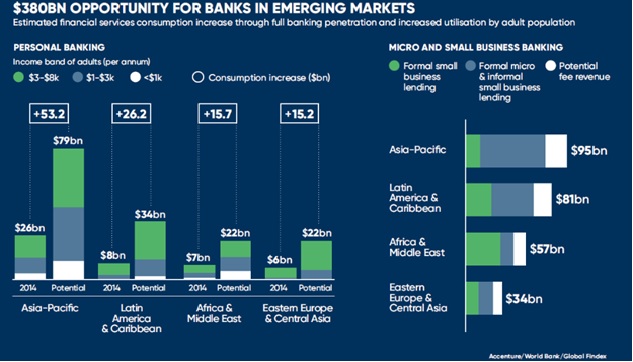
Global Financial Inclusion Disparities
- The World Bank’s 2021 Global Findex Database reveals significant global disparities in financial inclusion.
- Approximately 24% of adults lack access to formal financial accounts, with just 29% saving and 28% borrowing from formal institutions.
- Meanwhile, micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) face growing financing disparities.
- A World Bank report highlights that in developing countries, 21% of micro-enterprises struggle due to rejected loan applications or unfavorable terms.
- These findings highlight the need for inclusive financial policies and improved access to financial services to bridge these gaps and foster economic growth.
MSME Financing Gap: A Global Concern
- Globally, the financing gap for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) stands at 30%.
- According to the World Trade Organization’s MSME Day 2020 report, SMEs play a pivotal role, contributing around 35% to the GDP of developing economies and 50% in developed nations.
- Bridging this funding gap is imperative for stimulating global economic growth and creating productive employment opportunities.
Gender Disparities in Banking Access
- Around the world, women encounter enormous barriers including societal norms, mobility constraints, inadequate identification, and limited financial knowledge, hindering their access to fundamental banking services.
- This gender disparity is particularly pronounced in low-income and developing nations.
- Notably, in Sub-Saharan Africa and the Middle East and North Africa, the gender gap in bank account ownership stands at 12% and 14 % respectively—twice the emerging economy average and three times the global average.
- In developing countries, men with accounts are 6 % points more likely to use digital payments than women.
- Additionally, women often face challenges in accessing emergency funds.
- According to the World Bank’s Findex in 2021, 59% of men claimed they could consistently access emergency cash, while only 50% of women in developing nations reported the same ability.
B20 Taskforce: Promoting Financial Inclusion
- The B20 taskforce performed in-depth study on global financial inclusion, placing a special emphasis on the economic empowerment of disadvantaged groups including women, small companies, and farmers.
- They discovered 3 major pillars that comprised 11 important priorities.
- These topics cover efforts to lower obstacles to financial inclusion on both the supply and demand sides.
Pillar 1: Strengthening Financial Inclusion Ecosystem
- The ecosystem and facilitators that support financial inclusion must be strengthened.
- Modern financial inclusion attempts can be greatly hampered by a lack of innovation in the design and delivery of financial services, low levels of financial knowledge, a lack of viable options for growing capacity, and gender-based exclusion.
- Therefore, we concentrated on promoting gender-inclusive financial services and programs, strengthening the ability of people and small businesses through incubation and financial literacy instruction, and encouraging private sector participation in financial inclusion through partnerships.
Pillar 2: Expanding Financial Product Access
- Efforts to boost the availability of financial products and services are crucial.
- The Findex 2021 report underscored issues such as limited savings and restricted access to financial institutions.
- Furthermore, global insurance participation remains low, at just 7% of GDP.
- Accelerating financial inclusion for agricultural, rural, and migrant populations, who frequently encounter challenges in accessing timely and cost-effective financial services, is a priority.
To address these challenges, the focus has been on
- Lowering the capital costs for financial institutions.
- Developing innovative distribution channels for service delivery.
- Promoting standardized protocols to facilitate cross-border payments.
Pillar 3: Enhancing Consumer Protection and Innovation
- To retain customers’ confidence in innovative digital goods, we strengthened the framework for consumer protection while developing laws that achieve a balance between protection and innovation.
To back these pillars, the B20 task-force has recognized priority themes. Alongside this, they’ve outlined specific policy actions that can bring us closer to achieving 10 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and promote economic empowerment with inclusivity. In our presentation to the G20, we provide recommendations on these themes, highlighting practical examples and successful approaches to advance these goals.
Source: Mint
Mains Question
Discuss the significance of financial inclusion as a tool for reducing poverty and inequality on a global scale. Examine the role of international forums like the B20 in advancing financial inclusion?