Daily News Analysis.
Rajmash and Ramban Sulai Honey got GI Tags
Premium Bhaderwah Rajmash of Jammu is a red kidney bean that is smaller and distinct in texture. It has a sweet nuttier taste and is used to make a lot of delicious recipes. This Rajmash is grown as an intercrop with maize in Chinta Valley in Doda district.
Sulai honey, meanwhile is a premium and exotic variety of honey in Ramban. Known for its taste across the globe, this honey is extracted from Sulai plants grown in the Himalayas of Ramban, Doda.
What is geographical indication tags?
A geographical indication (GI) is a sign used on products that have a specific geographical origin and possess qualities or a reputation that are due to that origin. In order to function as a GI, a sign must identify a product as originating in a given place.
Benefits of GI Tag
- Prevents unauthorized use of a Registered Geographical Indication by others.
- It provides legal protection to Indian Geographical Indications which in turn boost exports.
- It promotes the economic prosperity of producers of goods produced in a geographical territory.
- GIs are protected under Paris Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property, geographical indications are covered as an element of IPRs.
- They are also covered Trade Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) Agreement, which was part of the Agreements concluding the Uruguay Round of GATT negotiations.
- In India is it issued by department of Industry Promotion and Internal Trade, Ministry of Commerce and Industry under Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration & Protection)Act, 1999 which was enacted by World Trade Organization (WTO).
Researched linked incentive schemes for the Pharma sector.
- News: Centre rolls out Rs 5,000 crore RLI scheme for pharma, and med-tech sectors to strengthen the research infra in the country and promote more industry-academia linkages for research and development (R&D).
- The government feels that with the right growth enablers, the Indian pharma industry can touch a 5 percent share of the global market by 2030 from the 3.4 percent now.
- The total outlay of the scheme would be Rs 5,000 crore over a period of five years from 2023-24 to 2027-28.
The Scheme has two components
- According to the Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers- The government is going to spend Rs. 700 crores on strengthening the research infrastructure by setting up Centres of Excellence at the National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education & Research (NIPERs). The Center of Excellence will strengthen the research infrastructure in pharma and med-tech sectors by providing advanced facilities to conduct research and will help in nurturing the talent pool by promoting industry-academia linkage.
- The second component deals with the promotion of research in the pharma and med-tech sector in six priority areas. The first product area is for new chemical or biological or phytopharmaceutical (natural) entities include complex generics, precision medicine (targeted innovative therapeutics), medical devices, orphan drugs (drugs for rare diseases), and drug development for antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
Typhoon Doksuri
News: Typhoon Doksuri roars into China, destroys power lines, uproots trees.
- Doksuri first struck Taiwan as a formidable Category 5 super typhoon, and subsequently made landfall in Fujian, China, maintaining its intensity as a Category 4 typhoon.
- It started as a low-pressure area in the Philippines, far off the coast of Mindanao.
- Typhoons are tropical cyclones that develop in the western Pacific Ocean and are equivalent in nature to hurricanes or cyclones found in other parts of the world.
- These weather phenomena are marked by their intensity, featuring rotating low-pressure systems that bring about powerful winds and heavy precipitation.
Formation and Life Cycle
- Typhoons originate over warm ocean waters, typically with temperatures of at least 26.5°C , primarily in tropical and subtropical regions.
- They begin as tropical depressions and gradually strengthen into tropical storms when their sustained wind speeds range from 39 to 73 mph.
- Once the wind speeds exceed 74 mph, the storm is officially classified as a typhoon.
Mahendragiri Warship
News: Vice President will launch India’s latest warship, Mahendragiri, at the Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited, Mumbai.
About Mahendragiri Warship
- The ship is named after a prominent mountain peak located in the Eastern Ghats of Orissa.
- Mahendragiri represents a technologically advanced warship, serving as a symbol of India’s commitment to honoring its maritime heritage.
- The ship is being built by the Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) in Mumbai.
- It is a Project 17A Frigates
About Project 17A
- Project 17A Frigates are an upgraded version of the Project 17 Class Frigates (Shivalik Class). They feature improved stealth characteristics, advanced weaponry, cutting-edge sensors, and enhanced platform management systems.
- The project involves four frigates being built by Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) in Mumbai and three by Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers Limited (GRSE).
- The design for Project 17A ships was developed in-house by the Indian Navy’s Warship Design Bureau (WDB).
- A significant portion, approximately 75%, of the equipment and systems for these frigates are sourced from domestic firms.
Mahendragiri Hills
- Location: Mahendragiri is a mountain in Odisha’s Gajapati district, situated in the Eastern Ghats at an altitude of 1,501 meters.
- Biodiversity: The region is known for its biodiversity, housing various medicinal plants and species. It serves as a transition zone between southern India and the Himalayas, promoting genetic diversity.
- Inhabitants: Mahendragiri is home to the Soura people, a vulnerable tribal group, and the Kandha tribe. Saura people, a Munda ethnic group, primarily reside in this region, speaking the Sora language.
- The Mahendragiri biosphere reserve is spread across an area of around 4,70,955 hectares.
First Domestic Reactor
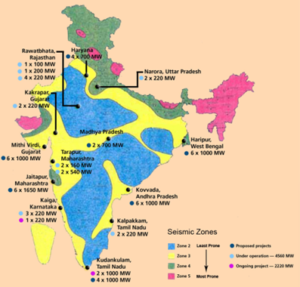
News India’s first domestically built 700 MW nuclear reactor, starts commercial operations in Gujarat.
- The reactor, named (Kakrapar Atomic Power Project) KAPP-3, began operating at 90 percent of its full power capacity on June 30, 2023.
- Additionally, KAPP-4, another domestically built 700 MW pressurized heavy water reactor (PHWR) at the Kakrapar site, is undergoing commissioning activities and has achieved rate of 96.92%.
- The Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited (NPCIL) is leading the development of the plants.
- There are now 22 Nuclear Power Plants in operation in India, with a combined capacity of 6780 MW.
- The largest Nuclear Power Plant in India is the Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant.
India’s three-stage nuclear program
- PHWRs: Use natural uranium, produce electricity, and yield plutonium-239 (Pu-239).
- FBRs: Utilize Pu-239 for increased energy output and fissile material production.
- Thorium-Based Reactors: Focus on thorium as fuel for sustainable energy production.
Chinese president is not visiting India for G20
News: Beijing has yet to confirm Chinese President Xi Jinping’s attendance at the G20 Summit in India on September 9-10.
India’s stance
- New Delhi is preparing to host Chinese Premier Li Qiang in case President Xi is unable to attend. This would mark Li’s first visit to India in his capacity as Premier.
- The uncertainty surrounding President Xi’s schedule has implications for G20 events and the joint communiqué, as consensus on issues, including the Russia-Ukraine conflict, is crucial.
- Despite the uncertainty, New Delhi plans to host the Chinese delegation, regardless of its leadership.
- Russian President Vladimir Putin will also not attend, sending Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov in his place, while other G20 leaders, including US President Joe Biden, have confirmed their participation.
- Xi last came to India in October 2019, when he went to Mamallapuram for the informal summit with Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
- Recent Chinese map controversy has created more havoc.
‘Meri Maati Mera Desh’ campaign
News Government has launched the ‘Meri Maati Mera Desh’ campaign as part of the ‘Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav’ celebration of India’s 75 years of Independence.
- Soil collected from various regions across the country will be utilized for the development of the Amrit Vatika Garden along the Kartavya Path in Delhi.
- A series of events are scheduled at various levels, spanning from panchayats and villages to states and the national level.
- Memorial plaques, known as Shilaphalakam, will be installed to honor the brave individuals who made the ultimate sacrifice.
- Citizens will take a pledge to reaffirm their commitment to the nation at the site.
- As part of ‘Vasudha Vandhan,’ 75 indigenous saplings will be planted in each gram panchayat or village.
- A special ‘Veeron Ka Vandan’ program will recognize and honor freedom fighters as well as the families of those who sacrificed for the nation’s independence.
NCERT
New: The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) has been granted the status of deemed university.
- An Institution of Higher Education, distinct from universities, excelling in a particular field of study, can attain the status of an ‘Institution Deemed-to-be-University’ upon the recommendation of the UGC and declaration by the Central government.
- These ‘deemed-to-be-university’ institutions are entitled to the academic recognition and privileges typically associated with a university.
- With the deemed university status, NCERT will offer its own graduate, postgraduate and doctoral degrees.
- Government also merged Bal Bhavans and Bal Vatika with the NCERT to “provide holistic education to children.”
NCERT
- NCERT is an autonomous organization established in 1961 by the Indian Government to advise on school education policies.
- Its main goals include conducting research in school education, producing educational materials, and offering teacher training.
- NCERT collaborates with state educational departments, universities, NGOs, and international organizations.
- It acts as a clearinghouse for educational ideas and supports the Universalization of Elementary Education.
- NCERT implements cultural exchange programs and provides training to educational personnel from other countries.