The need for an Indian system to regulate AI.
Relevance:
GS Paper- 3 Science & Technology
Tags: #AI #upsc #powerfultool #everydaylives #technology
Why in the News?
As Artificial Intelligence (AI) impacts our everyday lives, there has been a lot of discussion about how this exciting yet powerful and potentially problematic technology should be regulated.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
- Artificial Intelligence is a branch of Computer Science that is responsible for performing tasks commonly associated with human cognitive functions.
- These functions include interpreting speech, playing games, identifying patterns, generating arts etc.
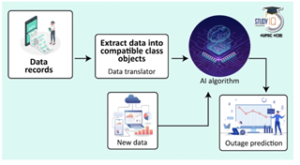
Working of AI
Why is there a need to regulate AI?
- Bias and discrimination: AI systems can inherit biases from the data they are trained on, leading to discriminatory outcomes. For example, facial recognition algorithms have been shown to have higher error rates for women and people with darker skin tones.
- Lack of transparency: Many AI algorithms operate as black boxes, making it difficult to understand how they reach their decisions. This lack of transparency raises concerns about accountability and the potential for unfair or biased outcomes.
- Lack of accountability: The responsibility and accountability for AI decisions can be unclear, especially when complex systems are involved. This poses challenges in determining liability in case of AI-related accidents or harm caused by AI systems.
- Privacy and data protection: AI systems often rely on vast amounts of personal data, raising concerns about privacy and data protection. Improper handling of data can result in unauthorized access, misuse, or breaches of sensitive information.
- Security risks: AI systems can be vulnerable to cybersecurity threats and attacks. Adversarial attacks can manipulate AI models to produce incorrect or malicious results, posing risks in critical domains such as autonomous vehicles or healthcare.
- Ethical considerations: AI raises ethical questions related to the impact on jobs, social inequality, and the concentration of power. For example, automated decision-making in hiring processes may perpetuate existing biases and result in unfair outcomes.
- Lack of regulation and standards: The rapid advancement of AI has outpaced the development of comprehensive regulatory frameworks and industry standards. This creates a regulatory gap and potential risks associated with unchecked AI development and deployment.
What are the various options for regulating AI?
- Soft law approach: Soft law approaches include options such as guidelines, best practices, industry standards, etc. This can be more flexible and adaptable to the rapidly evolving AI landscape. Soft law can provide initial guidance without imposing rigid regulations.
- Graduated regulation: Implement a regulatory framework that takes into account the size and capacity of AI companies. Differentiate between large, established companies and smaller startups, applying more stringent regulations to the former while allowing the latter some flexibility to encourage innovation.
- Regulatory sandboxes: Create regulatory sandboxes or controlled environments where startups and small companies can experiment with AI technologies under supervision. This allows for innovation while ensuring compliance with basic ethical and safety standards.
- Collaboration with the tech community: Engage with the tech community, including startups and small companies, in the regulatory process. The governments should seek input and feedback to better understand their unique challenges and ensure that regulations are practical and effective.
- A balance between hard and soft Law: Strike a balance between hard law (legislation and binding regulations) and soft law (guidelines and standards) to create a regulatory framework that is both enforceable and adaptable to technological advancements.
- Global regulatory cooperation: Foster international collaboration to establish a unified global regulatory framework for AI. This can involve engaging with other countries and international organizations to develop common standards, principles, and guidelines that can be adopted universally.
What are the advantages of regulating AI?
- Ethical use and accountability: Regulation ensures that AI systems are developed and deployed in an ethical manner, holding organizations accountable for their actions. This promotes responsible AI practices and prevents the misuse of AI technologies.
- Fairness and non-discrimination: Regulating AI can help address bias and discrimination by enforcing fairness principles. It ensures that AI systems do not disproportionately impact certain groups and promotes equal opportunities for all individuals.
- Consumer protection: Regulating AI protects consumers from fraudulent or deceptive practices. It ensures transparency and fairness in AI-driven products and services, enabling consumers to make informed decisions and seek redress in case of harm.
- International collaboration: Regulations facilitate international cooperation and harmonization of AI standards. This promotes consistency in ethical practices, fosters global collaboration, and addresses challenges associated with cross-border AI applications.
- Trust and public confidence: Regulations help build trust and public confidence in AI technologies by ensuring responsible and accountable use. This can lead to wider adoption of AI solutions and increased societal acceptance.
What are the challenges in regulating AI?
- Rapid technological advancement: AI is evolving at a rapid pace, making it challenging for regulators to keep up with the latest developments and effectively regulate a technology that is constantly evolving.
- Complexity and development: Regulating AI is challenging due to its complexity and the speed at which it develops. Creating effective regulations that address the intricacies of AI systems and keep pace with technological advancements can be difficult.
- Increased costs and competition: Compliance with regulations may impose additional costs on businesses, particularly smaller companies and startups, limiting their ability to compete in the AI market. The burden of regulatory compliance could disproportionately affect smaller players.
- Accountability and liability: Determining responsibility and liability when AI systems cause harm or make erroneous decisions can be challenging. Clarifying the legal frameworks and accountability structures surrounding AI is crucial for effective regulation.
- International cooperation: AI regulation requires international cooperation and collaboration to address global challenges, harmonize standards, and prevent regulatory arbitrage. Developing consensus among different countries with varying interests and priorities can be a complex task.
How global countries are planning to regulate AI?
Globally
- In February, the US launched an initiative to promote international cooperation on the responsible use of AI and autonomous weapons by militaries.
- Several forums such as the US-EU Trade and Technology Council (TTC), the Global Partnership in AI (GPAI), the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) are deliberating on the regulations of AI.
- The recent G-7 Leaders Communiqué also underscored the need for cooperation on AI, including on the impact of LLMs such as ChatGPT.
- Italy became the first Western country to ban ChatGPT out of privacy concerns, the EUis bringing in the AI Act this year, the US government released a blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights.
India is planning to regulate AI through several initiatives and frameworks
- Digital India framework: India is developing a comprehensive Digital India framework that will include provisions for regulating AI. The framework aims to protect digital citizens and ensure the safe and trusted use of AI.
- An ecosystem of modern cyber laws and regulations: India is constructing an ecosystem of modern cyber laws and regulations driven by the principles of openness, safety, trust, and accountability. These laws and regulations will provide a framework for governing AI technologies.
- National AI programme: India has established a National AI Programme to promote the efficient and responsible use of AI.
- National Data Governance Framework Policy: India has implemented a National Data Governance Framework Policy to govern the collection, storage, and usage of data, including data used in AI systems. This policy will help ensure the ethical and responsible handling of data in the AI ecosystem.
- Draft Digital India Act: The Ministry of Information Technology and Electronics is working on framing the draft Digital India Act, which will replace the existing IT Act. The new act will have a specific chapter dedicated to emerging technologies, particularly AI, and how to regulate them to protect users from harm.
Rest of the World
- European Union: The European Union is working on the draft Artificial Intelligence Act (AI Act) to regulate AI from the top down. The Council has published its position, and trials with the European Parliament are expected to begin. The goal is to finalize the legislation by the end of 2023.
- United States: The White House Office of Science and Technology Policy has published a non-binding Blueprint for the Development, Use, and Deployment of Automated Systems (Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights), listing principles to minimize potential harm from AI.
- Japan: Japan’s approach to regulating AI is guided by the Society 5.0 project, aiming to address social problems with innovation. The Integrated Innovation Strategy Promotion Council has published social principles for human-centric AI and guidelines for AI developers and companies. The Governance Guidelines for Implementation of AI Principles provide action goals and implementation examples for AI companies.
- China: China has established the “Next Generation Artificial Intelligence Development Plan” and published ethical guidelines for AI. The country has also introduced specific laws related to AI applications, such as the management of algorithmic recommendations.
What should be done?
- Establish comprehensive and flexible regulatory frameworks: The governments should develop clear guidelines and laws that address various aspects of AI, including data privacy, algorithmic transparency, accountability, and potential biases. These frameworks should be adaptable to the rapidly evolving nature of AI technology.
- Foster international cooperation: Given the global nature of AI and its potential impact, collaboration among countries is essential. International standards and agreements should be developed to promote ethical practices and ensure consistency in regulation across borders.
- Encourage industry self-regulation: Companies involved in AI development should take responsibility for ensuring the ethical and responsible use of their technologies. Self-regulatory initiatives can complement government regulations and demonstrate a commitment to safeguarding public interests.
- Promote transparency and explainability: AI algorithms and systems should be transparent, with clear explanations of their functioning and decision-making processes. This will enable users and regulators to understand how AI systems operate and detect potential biases or discriminatory outcomes.
- Invest in AI research and education: Governments, academic institutions, and industry stakeholders should allocate resources to research, development, and education in the field of AI. This will help create a well-informed workforce capable of addressing regulatory challenges and ensuring the safe and responsible deployment of AI technologies.
Way forward
- To make thoughtful and constitutionally tenable regulations, our leaders must educate themselves on the technology.
- The balance between technological gains and the harmful effect of the technology is a policy debate that will challenge governance all over the world.
- India could take the lead in conversations around global regulation for AI, as it hosts the G20 summit later this year.
Source: The Hindu
Mains Question
“Artificial intelligence is going to change every industry, but we have to understand its limits”. In light of this, discuss the benefits and challenges associated with AI in Indian context.