Daily News Analysis.
Mera Bill Mera Adhikar Scheme:
News: The long-awaited “Mera Bill Mera Adhikar” programme is anticipated to be introduced soon by the central government.
- Mera Bill Mera Adhikar Scheme is a Goods and Services Tax (GST) invoice incentive programme that offers cash incentives for uploading invoices.
- It would first be implemented in the UTs of Puducherry, Daman & Diu, and Dadra & Nagar Haveli, as well as the states of Assam, Gujarat, and Haryana.
- The goal is to persuade clients to ask for a bill each time they make a purchase.
- The program will apply to all bills sent to customers by GST-registered vendors.
- Winners would be eligible for cash reward awards ranging from Rs 10,000 to Rs 1 crore in a monthly and quarterly draw of lots.
- People may upload a maximum of 25 invoices every month, and the minimum purchase amount for an invoice to be eligible for the fortunate draw is Rs 200.
- There will be an Android and IOS version of the “Mera Bill Mera Adhikar” mobile app.
- The seller’s GSTIN, invoice number, amount paid, and tax amount should all be included on the invoice that is uploaded to the app.
Goods and Services Tax (GST)
The majority of products and services sold for domestic consumption are subject to the products and Services Tax (GST), which is a value-added tax. Consumers pay the GST, but businesses that sell the products and services are responsible for remitting it to the government.
Main GST Features
- Applicable In contrast to the previous concepts of manufacturing, selling, and providing services, GST is now only applied to the “supply” of goods or services.
- As opposed to the current premise of origin-based taxation, the GST is based on the destination-based consumption taxation principle.
- Dual GST is one in which both the federal government and the states simultaneously impose taxes on a same base. The GST that will be imposed by the Centre is known as Central GST (CGST), while the GST that will be imposed by the States is known as State GST (SGST).
- The Integrated Goods & Services Tax (IGST), in addition to any applicable customs charges, would apply to imported goods and services because they are deemed to constitute interstate supplies.
- The Centre and the States must agree on the CGST, SGST, and IGST tax rates before they may be implemented. On the GST Council’s advice, the rates are announced.
- Multiple Rates- At first, there were four rates for the GST: 5%, 12%, 16%, and 28%. The GST Council develops the schedule or list of goods that would be subject to these various slabs.
ASTRA Missile
News: On August 23, 2023, Tejas’ Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) LSP-7 successfully fired the ASTRA off the Goan coast.
- An indigenous Beyond Visual Range (BVR) air-to-air missile is the ASTRA Missile.
- Its purpose is to engage and obliterate nimble supersonic aerial targets.
- Defence Research and Development Laboratory (DRDL), Research Centre Imarat (RCI), and other DRDO institutions created and developed it.
- The domestic Tejas fighters shooting native Astra BVR is a significant step towards “Aatmanirbhar Bharat.”
Tejas LCA
- It is the smallest, lightest, and most maneuverable multi-role supersonic fighter in its class.
- This aircraft is built to accommodate a variety of precision-guided, air-to-air and air-to-surface missiles.
- It is capable of refilling from the air to the air. Tejas can carry a payload of up to 4000 kg. Mach 1.8. Is the speed of the missile.
Defence Research and Development Laboratory
- Modern missile systems and other technologies needed for the nation’s defense and deterrence are designed and developed by DRDL. Systems and technologies created by DRDL are used on platforms based in the air, sea, land, and underwater.
- Aerodynamics and Airframe Design, Computational Fluid Dynamics, Solid, Liquid, Ramjet and Scramjet Propulsion, Precision Fabrication, Systems Analysis, as well as Command and Control systems for missile-based weapon systems are just a few of the technologies that DRDL is currently working on.
Equal Contrast Technique (ECT)
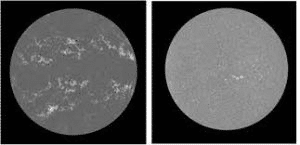
News: Equal Contrast Technique (ECT), a novel technique created by scientists to evaluate photographs of the Sun in white light, can help prevent temporal and latitudinal fluctuations in observations caused by instrument and sky circumstances.
- It is well known that the sun has a significant number of weak magnetic field zones that change over time.
- Since there is a significant correlation between the magnetic field and the Ca-K line intensity of the location on the Sun, they can be investigated using magnetograms and Ca-K line photographs of the sun.
- The magneto-grams are only available for brief periods of time, and the instrument’s properties change over time.
- At Kodaikanal Observatory (KO), Ca-K line images have remained accessible for more than 100 years with no changes to the instrument’s optics.
- Similar information has been available for roughly 70 years at various observatories across the world, including Mount Wilson Observatory (MWO).
- For the first time, researchers have demonstrated using data from Kodaikanal Observatory that the association between derived plage area—a bright region in the sun’s chromosphere—and sunspot number is excellent, even on a daily basis, over a period of nearly 100 years.
- This kind of precise study of the historical time series of Ca-K pictures can be beneficial for a trustworthy and accurate investigation of changes in the sun and their impact on the earth’s climate.
- It aids in comprehension of solar dynamics, variations in the solar cycle, dynamo operations in the convection zone, and the ensuing long-term climate changes on Earth.
Microsites Project
News: The Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) will be implemented more quickly across the nation thanks to the 100 Microsites projects that the National Health Authority (NHA) announced. The microsites initiative identifies certain geographic areas where targeted outreach is conducted to recruit small- and medium-sized private healthcare providers.
Facilities that fall under a microsite’s purview
- Private healthcare facilities that generate health records include standalone clinics, polyclinics, nursing homes, small hospitals (ideally with less than 10 beds), labs, pharmacies, and any other healthcare facilities.
- Health Care Facilities and Medical Staff from all medical specialties. According to the regional priorities, any State/UT may opt to implement any of the following kinds of Microsites.
- A microsite classified as Category A contains at least 1000 establishments, including all the aforementioned sorts of healthcare institutions.
- Category B Microsite– A microsite that includes all of the aforementioned sorts of health facilities and has at least 500 but fewer than 1000 facilities.
- State Mission Directors of ABDM would be primarily responsible for implementing these Microsites, with NHA providing funding and overall direction.
- An on-the-ground team will be provided by an interface agency as part of this program to contact local healthcare providers. This group will raise awareness of the advantages of ABDM.
- In addition to encouraging the use of ABDM to provide digital solutions for routine clinical documentation, it will assist the service providers in joining the core registries under ABDM.
Chandrayaan-3 Successfully Lands On Moon’s South Pole:
News: Being the first mission to soft-land on the lunar south pole, an area that had never been investigated, Chandrayaan-3 made history.
- The mission’s objectives were to show off rover mobility, a gentle and secure lunar landing, and in-situ scientific research.
- India is now one of just a handful of nations to have successfully landed on the moon, joining the US, Russia, and China.
- After the disappointment of the Chandrayaan-2 mission’s unsuccessful landing in 2019, Chandrayaan-3’s successful landing followed.
- Chandrayaan-2’s Vikram lander crashed on the moon’s surface as a result of losing control and communication during descent. On the lunar surface, Chandrayaan-3 is planned to run for at least one lunar day.
- Within a 500-meter circle surrounding the landing site, the Pragyan rover will move while carrying out experiments and transmitting data and pictures to the lander.
- The orbiter will transfer the information and pictures to Earth after receiving them from the Vikram lander. Advanced scientific payloads are combined between the Rover and Lander modules.
- These tools are made to undertake thorough examinations into a variety of lunar properties, including terrain analysis, surface chemistry, mineralogical composition, atmospheric parameters, and, most importantly, the search for water and prospective resource reserves.
- A Spectro-polarimetry of Habitable Planet Earth (SHAPE) payload is also on the propulsion module that propelled the lander and rover configuration into a 100 km lunar orbit in order to analyze the spectral and polarimetric measurements of Earth from the lunar orbit.