LESSONS FROM INDIA’S ALTERNATE DEVELOPMENT PLAN
Relevance: GS 3 – Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
Why in the News?
- Investment in energy transition is driving India towards a green and sustainable future.
- Female empowerment initiatives and Digital public infrastructure development is playing a key role in India’s progress.
- India’s development showcases the positive impacts of both public and private sector
- Innovative approaches and resilience in India’s development can serve as a model for other countries.
India’s Economic Growth
- India demonstrated a 5% growth in the past fiscal year, standing out amidst a weak global outlook.
- This growth is primarily fueled by public investments but is significantly influenced by the private sector.
- Role of Private Sector: Private companies are actively investing in a green and sustainable future. Women entrepreneurs in Tamil Nadu exemplify the importance of empowering women for a country’s development.
- India’s Development Impact: India’s development path showcases the positive impacts of both public and private sector initiatives. It serves as a model for other countries, demonstrating innovation and resilience.
- Knowledge Sharing and Learning: India provides practical development insights at federal, state, and local levels. It offers a unique platform for testing and scaling real-world solutions through South-South knowledge exchange.
- Focus Areas of Demonstration Effect
- Energy Transition: India is making significant strides in transitioning towards sustainable energy sources.
- Digital Public Infrastructure: Development in this area is shaping India’s future and facilitating digital transformation.
- Female Empowerment: Initiatives are in place to empower women, showcasing the potential of women-led development strategies.
India’s Progress in Energy Transition
- Renewable Energy Growth
- Renewable energy accounts for 42% of India’s total power generation capacity.
- India is the world’s fourth-largest renewables market and has 3% of global solar manufacturing capabilities.
- Investment in Renewables
- India has invested nearly $10 billion annually in renewables over the past five years.
- It ranks among the top five emerging and middle-income economies with significant public investment in renewable energy.
- Support for Electric Vehicles and Green Hydrogen
- India is promoting the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and the production of green hydrogen.
- Investment Opportunities
- Investors recognize India’s clean energy shift as a major opportunity.
- The World Bank has invested approximately $1 billion in solar parks and rooftop solar, leveraging 40 times that amount in commercial investment.
- Next Phase of Energy Transition
- Future efforts will focus on addressing renewable energy intermittency through investments in transmission and storage.
- Prioritizing rapid electrification of transportation and fostering industrial decarbonization are key objectives.
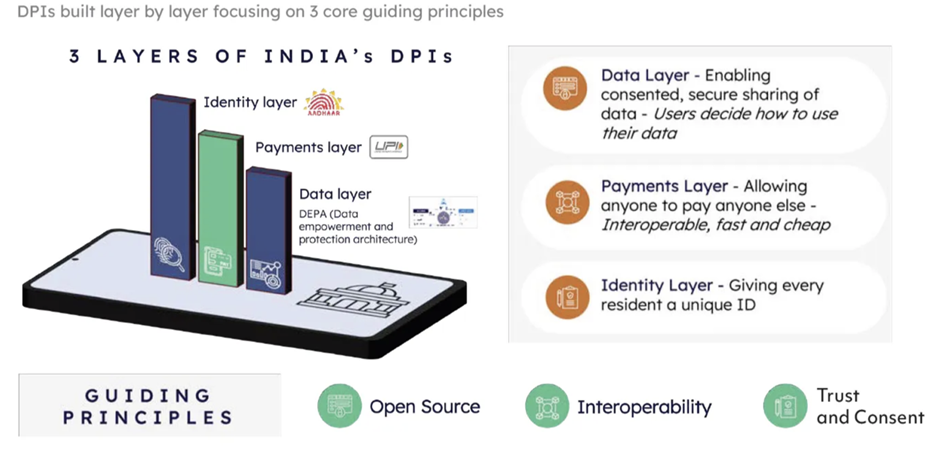
Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) Initiative in India
- Technology for Inclusion
- India has pioneered the use of technology to promote inclusion.
- Digitally verifiable proof of identity allows millions to access social safety net payments, open bank accounts, and receive government services efficiently.
- Impact on Public Services
- Digital payments have reduced delays in maternal health conditional cash transfers by 43%.
- Women micro-entrepreneurs in Tamil Nadu are benefiting from a cashless environment, utilizing digital networks to expand their businesses.
- Transformation of Rural Communities
- Digital innovation is driving transformation in rural communities, enabling online health consultations, remote learning, e-commerce, and fintech services.
- Lessons for Other Countries
- India’s experience with DPI offers valuable insights for countries looking to leverage the digital economy for growth, inclusion, and poverty reduction.
- The World Bank is actively sharing India’s DPI journey to inspire and guide other nations.
Progress in Female Labour Force Participation in India
- Encouraging Signs
- Despite lagging behind in female labour force participation compared to other countries, there are encouraging signs of change in India.
- Women in Diverse Roles
- Women farmers, entrepreneurs, industrial workers, and public officials are actively working to bridge the gender gap.
- Impact of Policies in Tamil Nadu
- Policies encouraging investment in safe urban housing have positively influenced women’s entry into the workforce.
- Improved access to finance has boosted female labour force participation in the industry to 43% of the national total.
- National Rural Livelihoods Mission
- Supported by the World Bank, this initiative has empowered millions of rural women by organizing them into self-help groups.
- Over $4 billion in commercial credit has been mobilized to support women-led cooperatives and rural enterprises.
- Potential for Growth
- If India scales these experiences, it could potentially raise its female labour force participation to the developing country average of 50%.
- This could add a full percentage point to India’s potential growth rate and uplift a generation of Indian women and girls.
Lessons Learned and Future Outlook
- Valuable Lessons from India
- The World Bank rolls out reforms to scale and replicate impactful projects across emerging and developing economies.
- India’s Role in Global Development
- With the world’s largest population and an aspiration to reach high-income country status by 2047, India will continue to play a crucial role in shaping global development narratives.
Mains question
How can India’s experiences in energy transition serve as a model for other emerging and developing economies? (Word Limit: 250 words)