Daily News Analysis.
CE-20 Cryogenic Rocket Engine: Successfully Tested For Mission Gaganyaan (GS-3)
News: The cryogenic rocket engine that will be used in the Indian Space Research Organization’s ‘Mission Gaganyaan’ has been successfully tested by the Liquid Propulsion Research Centre (IPRC) at Mahendragiri.
- The Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC), an ISRO unit, created and developed the CE-20 cryogenic engine.
- It will drive the LVM3 launch vehicle’s Cryogenic Upper Stage. For its ‘Mission Gaganyaan’ to launch a man into space in 2024, ISRO would employ it.
- The gas-generator cycle is a first for an Indian cryogenic engine. It is one of the world’s most potent upper-stage cryogenic engines. In vacuum, this engine produces a nominal thrust of 186.36 kN.
- Due to the usage of propellants at very low temperatures and the resulting thermal and structural issues, the cryogenic stage is technically a very complex system.
- It burns liquid fuels that are chilled to extremely low temperatures (Oxygen liquefies at -183 degrees Celsius and hydrogen at -253 degrees Celsius).
- In comparison to solid and earth-storable liquid propellant rocket stages, a cryogenic rocket stage is more effective and produces more thrust for every kilo-gramme of propellant it burns.
Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO)
- The space agency for India is called the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO). The organization works in science, engineering, and technology to help India and humanity benefit from space.
- The Department of Space (DOS) of the Indian government includes ISRO as a key component. The department primarily uses different ISRO Centres or Units to carry out the Indian Space Programme.
- The Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR), which was founded by the Indian government in 1962 as Dr. VikramA Sarabhai’s idea, was the predecessor to ISRO.
- On August 15, 1969, ISRO was established, replacing INCOSPAR with an expanded mandate to utilize space technology. In 1972, DOS was established, and ISRO was included in DOS.
- The development and use of space technology for diverse national needs is ISRO/DOS’s main goal.
- Major space systems for communication, television broadcasting, and meteorological services, resource monitoring and management, and space-based navigation services have been built by ISRO to achieve this goal.
- To place the satellites in the necessary orbits, ISRO has created the PSLV and GSLV satellite launch vehicles.
India’s 6th Minor Irrigation Census (GS-3)
News: The sixth census of minor irrigation schemes (with the reference year 2017–18) has been made public by the Ministry of Jal Shakti, providing insight into the state of irrigation practices throughout India. Five censuses have been undertaken thus far in the years 1986–87, 1993–94, 2000–01, 2006–07, and 2013–14.
Report highlights include
- There have been reported to be 23.14 million MI schemes across the nation. There are 1.21 million (5.2%) surface water (SW) systems and 21.93 million (94.8%) groundwater (GW) projects among them.
- The majority of MI projects use dug wells, which are followed by shallow tube wells, medium tube wells, and deep tube wells.
- Compared to the previous census, there were 1.42 million more MI schemes according to the 6th MI census.
- GW schemes climbed by 6.9% nationally, while SW schemes increased by 1.2%. India’s MI schemes are most popular in Uttar Pradesh, followed by Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu.
- Maharashtra is the top-performing State in terms of surface flow, surface lift, and dug-wells. Punjab, Karnataka, and Uttar Pradesh are the top three States for shallow, medium, and deep tube wells, respectively.
- The highest shares of SW schemes are in Maharashtra, Karnataka, Telangana, Odisha, and Jharkhand. A little over 96.6% of MI projects are privately owned. 98.3% of GW projects and 64.2% of SW schemes are owned by private companies, respectively.
- Data on the gender of MI scheme owners was gathered for the first time. Women own 18.1% of the privately held schemes. A single source of funding provides funding for about 60.2% of initiatives.
- Individual farmers’ own resources make up a sizable portion of the finance (79.5%). 39.8% of schemes have several funding sources.
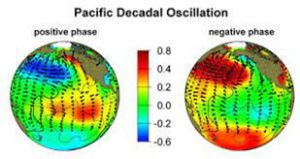
Pacific Decadal Oscillation: (GS-3)
News: According to a new study, the Pacific Decadal Oscillation, a cyclical phenomenon that occurs every 20–30 years, may increase the frequency of cyclones that develop near the equator in the coming years.
- A long-term ocean oscillation in the Pacific Ocean is known as the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO). At the University of Washington, Steven Hare first used the term PDO about 1996.
- Only after monitoring ocean temperatures and their interactions with the atmosphere for a number of years can this be known. The PDO waxes and wanes every 20 to 30 years on average.
- Scientists can identify whether we are in a “cool” phase or a “warm” phase based on information about ocean surface topography and other ocean and atmospheric data.
- The cool phase is marked by a warm horseshoe pattern of higher-than-normal sea-surface heights connecting the north, west, and southern Pacific and a cool wedge of lower-than-normal sea-surface heights/ocean temperatures in the eastern equatorial Pacific.
- When the west Pacific Ocean cools while the wedge in the east heats, this is known as the “warm” or “positive” phase. The jet stream’s route is altered by where the cold and warm water masses are located.
- Storms sweep across the United States thanks to the jet stream in the northern hemisphere.
Neeraj Chopra – World Champion
News: Neeraj Chopra made history, securing India’s first gold at 2023 World Athletics Championships in Budapest, Hungary.
- Chopra threw 88.17m in his second attempt to top the leaderboard. The silver medal went to Pakistan’s Arshad Nadeem (87.82m) and the bronze medal to the Czech Republic’s Jakub Vadlejch (86.67m).
- Chopra’s victory is a major achievement for Indian athletics. It is a sign that India is producing world-class athletes in track and field.
- Anju Bobby George was the only athlete from India to take home a medal at the World Athletics Championships in 2003 after taking home the bronze in the long jump category.
- Chopra’s success will inspire other young athletes in India to pursue their dreams.
Neeraj Chopra
- Born on December 24, 1997, in Khandra, Haryana, India
- Neeraj Chopra initially pursued discus throwing but transitioned to javelin in 2015.
- He achieved Gold at the 2016 IAAF World U20 Championships and 2018 Asian Games.
- In the 2020 Tokyo Olympics, he made history as India’s first athletics Olympic gold
- He secured Silver at the 2022 World Athletics Championships in Oregon.
Maharashtra’s First Vulture Center
News: Maharashtra’s First Vulture Conservation and Breeding Center to Be Established Near Pune’s Pingori, 60km Away.
- First vulture conservation and breeding center in Maharashtra’s Pingori, near Pune, on the occasion of International Vulture Awareness Day( 2nd September).
- Center is being initiated by the Ela Foundation, known for its expertise in ornithology and conservation efforts for critically endangered vulture species in Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh.
- Initiative aligns with the Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change’s Action plan for vulture conservation in India (2020-2025).
- The center will focus on breeding critically endangered vultures and supporting in-situ conservation .
Vulture
- Vultures are a group of large scavenging birds known for their role in cleaning up the environment by feeding on carcasses.
- They play a crucial ecological role in disposing of animal remains and preventing the spread of diseases.
- Habitat: Deserts, savannas, and grasslands close to water sources are the vulture’s favored habitats. It can also be found living in open mountain ranges that are up to 3,000 meters above sea level.
Action Plan for Vulture Conservation in India (2020-2025)
- Developed by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change in consultation with experts from the wildlife conservation community.
- A comprehensive plan to conserve vultures in India by reducing diclofenac use, creating vulture safe zones, and increasing food availability.
Central Gujarat water storage decreases; major dams green
News: Central Gujarat shows a decrease in water storage, but main dams are in good condition.
- Central Gujarat is experiencing a decrease in water storage due to a rainfall deficit in August.
- As of now, the 17 dams in the region are at 47.39% of their total capacity, compared to 80% on September 1, 2022.
- This decline in storage is particularly affecting districts like Vadodara, Anand, Kheda, Dahod, Mahisagar, and Chhota Udepur, which have faced rainfall shortages, resulting in a storage shortfall of 761.48 million cubic meters compared to the previous year.
- Vadodara, with a daily water demand of 620 million liters, is hoping that its Ajwa reservoir will reach its maximum level of 212 feet, currently at 208 feet.
- However, the Sardar Sarovar Dam and the Karjan Dam in Narmada district are in better shape, at 82.09% and 76.6% of their total capacity, respectively.
- Despite the rainfall pause, the Sardar Sarovar Dam is still progressing toward its full reservoir level, thanks to inflows from Madhya Pradesh.
- The dam currently releases water for irrigation while generating hydropower.
- Overall, water reservoirs in central Gujarat are facing a deficit, while other regions in the state have varying levels of water storage.
NCW demands report on Pratapgarh disrobing.
News: NCW strongly condemns Rajasthan Pratapgarh incident, where woman allegedly molested and video recorded, demands swift action.
National Commission for Women
- The National Commission for Women (NCW) was established following recommendations from the Committee on the Status of Women in India (CSWI) nearly 50 years ago.
- It was created to serve as a statutory body under the National Commission for Women Act, 1990, and officially began its operations in January 1992
- Jayanti Patnaik appointed as 1st President of National Commission For women
- Core mission: To promote women’s equality and ensure their active participation in all aspects of life by securing their rights and entitlements through policy formulation, legislative initiatives, and other suitable means.
- Primary functions: Encompass reviewing the existing constitutional and legal safeguards for women, suggesting necessary legislative reforms, facilitating the resolution of women’s grievances, and providing policy advice to the government on matters affecting women.
- Composition consists of a chairperson, a member secretary, and five other members, with the chairperson nominated by the Central Government.
- Over the years, the NCW has played a vital role in addressing women’s issues, including taking action on numerous complaints and proactively engaging in various initiatives aimed at promoting women’s rights and well-being.
- This includes advocating against practices like child marriage and reviewing important laws such as the Dowry Prohibition Act, 1961, the Pre-Conception and Pre-Natal Diagnostic Techniques Act 1994 etc.
Arunachal bans Glue traps
News: Arunachal Pradesh bans glue traps, joining 16 other states, prohibiting their manufacture, sale, and use against rodents.
- The Arunachal Pradesh government has responded to an appeal from People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals (PETA) India by issuing a state-wide prohibition on the manufacture, sale, and use of glue traps for catching rodents.
- This move aligns with advisories from the Animal Welfare Board of India (AWBI) and follows similar bans in 16 other Indian states.
- The ban on glue traps has already been implemented by the governments of Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Goa, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Karnataka, Ladakh, Lakshadweep, Madhya Pradesh, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Sikkim, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Uttarakhand, and West Bengal.
- PETA India’s praised the government for its efforts to protect animals, emphasizing that glue traps cause slow and painful deaths to not only rodents but also non-target animals like birds, squirrels, reptiles, and frogs.
- The use of glue traps is deemed a punishable offense under the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (PCA) Act, 1960, and a violation of the Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972, which prohibits the hunting of protected indigenous species.
- PETA India suggests that a more humane approach to rodent control is to make areas unattractive to rodents, eliminate food sources, and use non-lethal deterrents such as ammonia-soaked cotton balls or rags.
Glue Trap
- A glue trap is a type of pest control device designed to capture and immobilize rodents and other small animals
- When they try to cross the glue boards, little animals become stuck to them by their feet or by their fur. Once trapped, the animals are helpless to free themselves.
- Animals caught in glue traps often suffer from hunger, dehydration, suffocation, or injuries while attempting to escape.
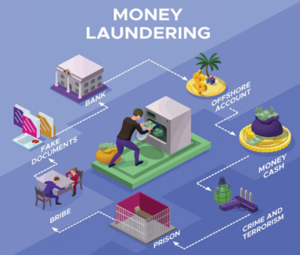
ED arrest Goyal in bank fraud case
News: ED detains Jet Airways founder Naresh Goyal in a case involving money laundering ,Bank fraud.
- Money laundering is the process of concealing the illegal origins of funds by making them appear legitimate through a series of complex financial transactions.
- It is regarded as a crime in India, and the charges in this case are supported by the rules laid out in the 2002 Prevention of Money Laundering Act.
Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA)
- In response to India’s international commitment (Vienna Convention) to tackle the threat of money laundering, the PMLA was passed.
Objectives
- prevention of money laundering.
- preventing the flow of money into unlawful and fraudulent business practices.
- allowing for the confiscation of goods used for money laundering or resulting from it.
- addressing any additional issues pertaining to or incidental to the act of money laundering.
Applicability
- The PMLA applies universally to individuals, companies, partnerships, associations, corporations, as well as any affiliated agencies, offices, or branches under their ownership or control.
- Offenses under PLMA: Prevention of Corruption Act, Narcotics Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, Antiquities and Art Treasures Act, Trademark Act, Wildlife Protection Act, Copyright Act and Information Technology Act, trans-border crimes.
Enforcement Directorate (ED)
- The Enforcement Directorate (ED) is an Indian law enforcement and economic intelligence agency under the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance.
- Its roots trace back to May 1, 1956, when an ‘Enforcement Unit’ was established within the Department of Economic Affairs to address violations of Exchange Control Laws under the Foreign Exchange Regulation Act, 1947.
- The ED’s primary mission is to enforce two pivotal Acts of the Indian government: the Foreign Exchange Management Act 1999 (FEMA) and the Prevention of Money Laundering Act 2002 (PMLA).